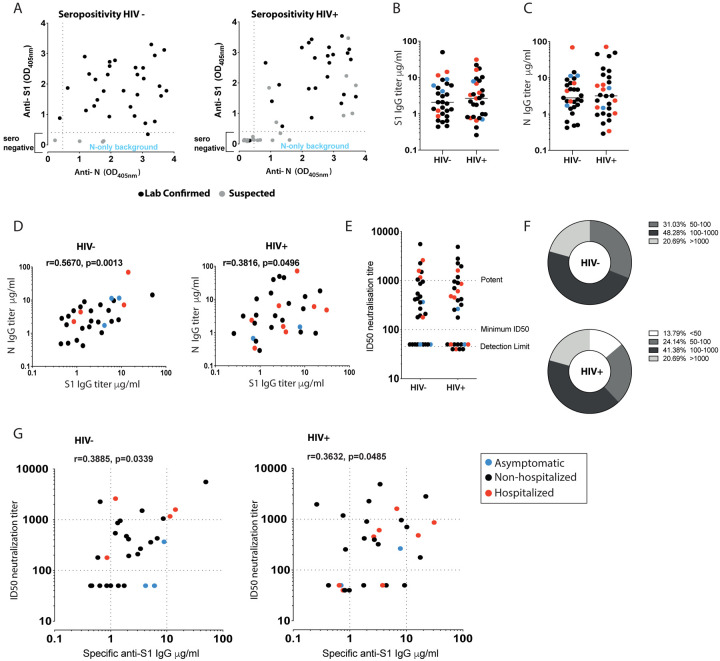
Fig. 1. Antibody response in HIV positive and negative donors recovered from COVID-19 disease.
(A) Seropositivity screen of plasma samples for antibodies against the external Spike antigen, using a recombinant Spike S11–530 subunit protein (S1), and against the full-length internal Nucleoprotein (N) antigen to confirm prior infection in HIV negative and positive donors. A sample absorbance greater than 4-fold above the average background of the assay was regarded as positive. Black dots denote laboratory confirmed cases and grey dots suspected/household contacts. (B) Comparison of S1 IgG and N IgG antibody titers in HIV negative and (C) HIV positive donors. Red dots: hospitalized cases; Black dots: mild (non-hospitalized cases); blue dots: asymptomatic cases. (D) Correlation between S1 IgG and N IgG titers in HIV negative and positive donors. (E) Neutralization titers in HIV negative and positive donors. Dotted lines indicate detection limit, minimum ID50 and potent levels >1000. (F) Proportion of HIV negative and positive donors with neutralizing antibodies within the given ranges. (G) Correlation between S1 IgG titers and neutralization titers in HIV negative and positive donors. The non-parametric Spearman test was used for correlation analysis. *p < 0.05, **p<0.01