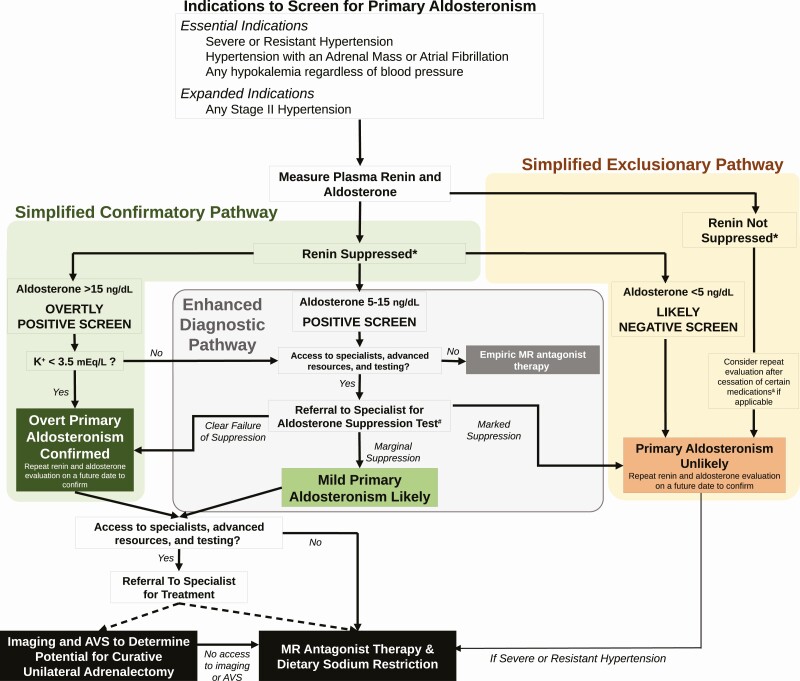
Figure 1.
Simplified diagnostic algorithm for primary aldosteronism. *There is no uniform definition for suppressed renin. A suppressed, or very low, plasma renin activity or renin concentration is necessary to confirm renin-independent aldosteronism that characterizes primary aldosteronism. A suppressed renin is defined as a plasma renin activity of less than 0.6 ng/mL/h, although a more liberal definition of less than 1.0 ng/mL/h can be used. Alternatively, a renin concentration of less than 5 mU/L is considered suppressed, although a more liberal definition of less than 8.2 mU/L can be used. #The most recommended and widely used dynamic confirmatory tests include the oral sodium suppression test, the seated intravenous saline suppression test, the fludrocortisone suppression test, and the captopril challenge test. &Therapeutic doses of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists and/or epithelial sodium channel inhibitors can induce an increase in renin in patients with primary aldosteronism. Less commonly, high doses of loop diuretics may induce this increase in renin as well. Rarely, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers can similarly increase renin in patients with primary aldosteronism. When the pretest probability for primary aldosteronism is reasonably high, a medication washout for 4 weeks, followed by repeat renin and aldosterone measurement, can be conducted to assess the true renin phenotype. AVS, adrenal venous sampling; MR, mineralocorticoid receptor.