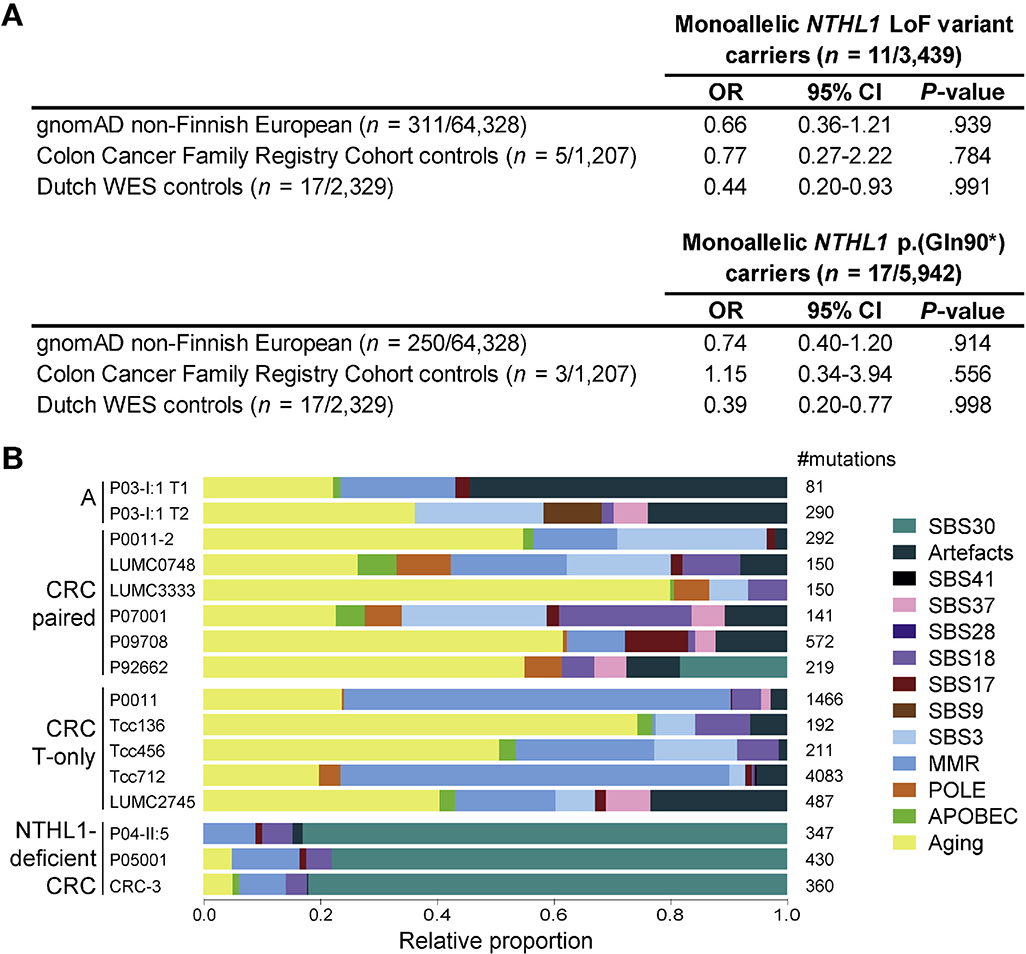
Figure 1.
Enrichment and mutational signature analysis of NTHL1 LoF variants in individuals with polyposis and/or CRC (case patients). (A) Frequencies of germline monoallelic NTHL1 LoF variants and monoallelic NTHL1 p.(Gln90*) variants in individuals with polyposis and/or CRC (case patients) compared with control populations. (B) Mutational signature analysis of tumors from carriers with a monoallelic NTHL1 LoF variant. Mutational signatures with shared etiologies were grouped for display purposes, which are the signatures associated with aging (SBS1, SBS5, and SBS40), DNA mismatch repair deficiency (SBS6, SBS15, SBS20, SBS21, SBS26, and SBS44), Polymerase Epsilon (POLE) exonuclease domain deficiency (SBS10a and SBS10b), Apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme (APOBEC) activity (SBS2 and SBS13), and artifact signatures (SBS45, SBS51, SBS52, SBS54, and SBS58). Data availability: paired: tumor and normal or tumor data were available; T-only: only data from 1 tumor tissue were available. A, adenomatous polyp; CI, confidence interval; OR, odds ratio.