Figure 2.
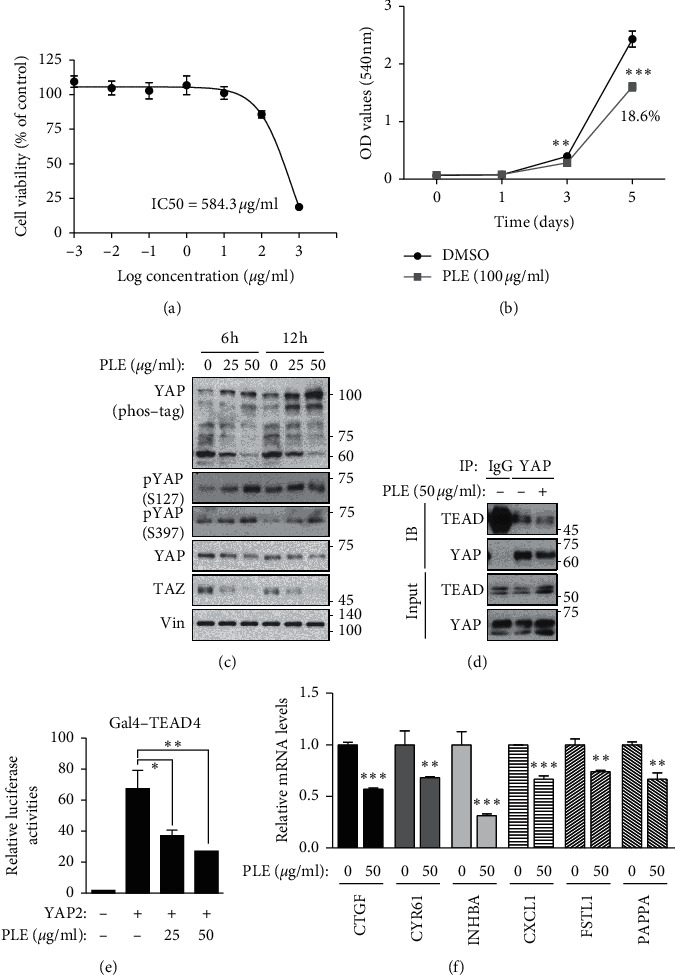
PLE inhibits YAP activity and disrupts YAP-TEAD complex to inhibit its transcriptional activity. HEK293A cells were treated using the indicated concentrations of PLE for 24 h. (a) Cell viability was measured using an EZ-Cytox cell viability assay kit. IC50 values were calculated from concentration response curves using Prism 5.0 software. The IC50 value of HEK293A cells was 584.3 μg/mL. Error bars represent ± SEM from n = 3 per group. (b) HEK293A cells were treated with DMSO and 100 μg/mL of PLE for 5 days, and cell proliferation was measured by SRB assay at an absorbance of 540 nm. The proliferation of HEK293A cells with PLE was decreased by 18.6% compared with control cells. Error bars represent mean ± SEM (n = 3). ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01; Student's t-test (unpaired, one-tailed) was used for statistical analysis. (c) HEK293A cells were treated with various concentrations (50 and 100 μg/mL) of PLE for 2 and 6 h, YAP phosphorylation states were determined by phos-tag gel shift assay, and cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with anti-YAP, pYAP, TAZ, and Vin. (d) HEK293A cells were treated with PLE (50 μg/mL) for 6 h. Endogenous YAP/TAZ was immunoprecipitated, and the co-precipitated pan-TEAD was detected by western blot. (e) HEK293A cells were co-transfected with 5 × UAS-luciferase reporter, Gal4-TEAD4, Renilla, with or without HA-YAP2. HEK293A cells were treated with PLE in a concentration-dependent manner. Cells were harvested 10 h after treatment. Representative results of a single experiment with n = 3 biological replicates; three independent experiments were carried out. (f) HEK293A cells were treated with 50 μg/mL of PLE for 12 h before harvesting. mRNA levels of CTGF, CYR61, INHBA, CXCL1, FSTL1, and PAPPA were determined using RT-qPCR. Bars represent mean ± SEM (N = 3). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001; Student's t-test (unpaired, one-tailed) was used for statistical analysis.
