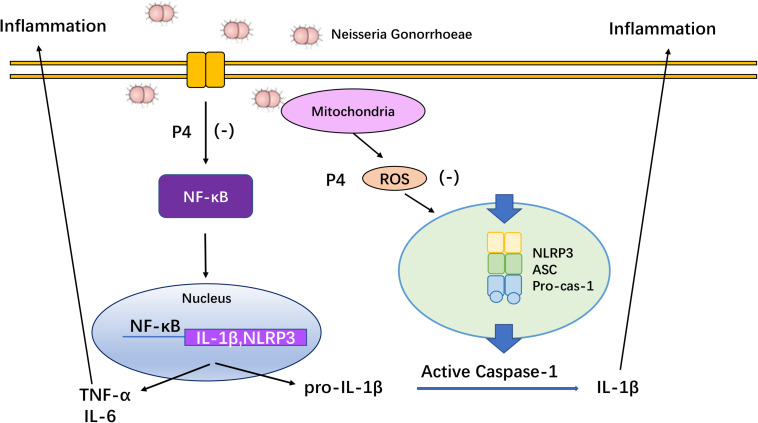
FIGURE 8.
Overview of mechanisms by which progesterone inhibited NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome activated by N. gonorrhoeae. Progesterone inhibits N. gonorrhoeae induced-inflammation in murine models and macrophages through (1) inhibiting the activation of NF-κB signal pathway, thus decreasing NLRP3 and pro-IL-1β expression; (2) suppressing ROS production, thus inhibiting caspase-1 activation and IL-1β/IL-18 secretion.