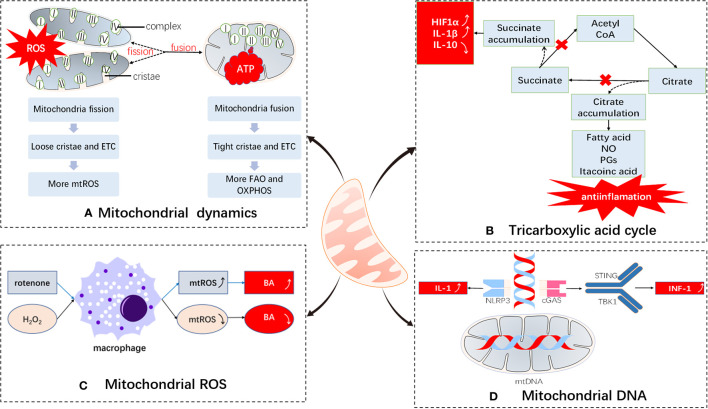
Figure 1.
Immunomodulatory effects of mitochondria. Mitochondria undergo (A) dynamic changes: The electron transport chains of split and fused mitochondria are different and tend to produce ROS and ATP, respectively; (B) metabolic medium of the tricarboxylic acid cycle: blockade of the tricarboxylic acid cycle leads to accumulation of inflammatory substances; (C) ROS production: mitochondrial ROS are important bactericidal substances of macrophages; (D) DNA damage participates in immune regulation: mtDNAs participate in immune responses by serving as DAMPs. ETC, electron transport chain; BA, bactericidal; ROS, reactive oxygen species; FAO, fatty acid oxidation; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; NLRP3, NACHT, LRR, and PYD domain-containing protein 3; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; cGAS, cyclic GMP-AMP synthase; STING, stimulator of interferon genes; TBK1, TANK-binding kinase 1.