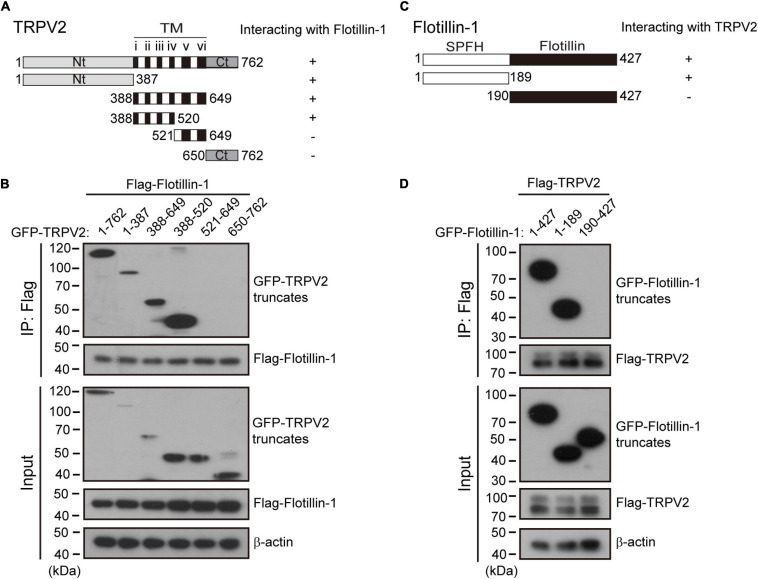
FIGURE 6.
Identification of interaction domains for the association between TRPV2 and flotillin-1. (A) A schematic representation of full-length TRPV2, its mutants that were studied, and their abilities to interact with flotillin-1. The number denotes the position of the amino acid residues. (B) N-terminal region and transmembrane domains 1–4 of TRPV2 are responsible for the interaction between TRPV2 and flotillin-1. HEK 293T cells were transiently transfected with different truncation mutants tagged with GFP and flotillin-1-Flag as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag agarose beads and analyzed by IB using anti-GFP and anti-Flag, respectively. Whole-cell lysates were also used for IB with anti-GFP and anti-Flag for input. (C) Schematic diagram of composition of mutant flotillin-1 including SPFH domain (aa 1–189), and flotillin domain (aa 190–427), and as well as their abilities to interact with TRPV2. (D) HEK 293T cells were transfected with TRPV2-Flag and different mutant flotillin-1 fused with GFP as indicated. Cell lysates were subjected to IP by anti-Flag, followed by IB for anti-GFP and anti-Flag, respectively. Note, molecular weight standards (in KD) are shown on the left. TM, transmembrane. Data are representative of three independent experiments.