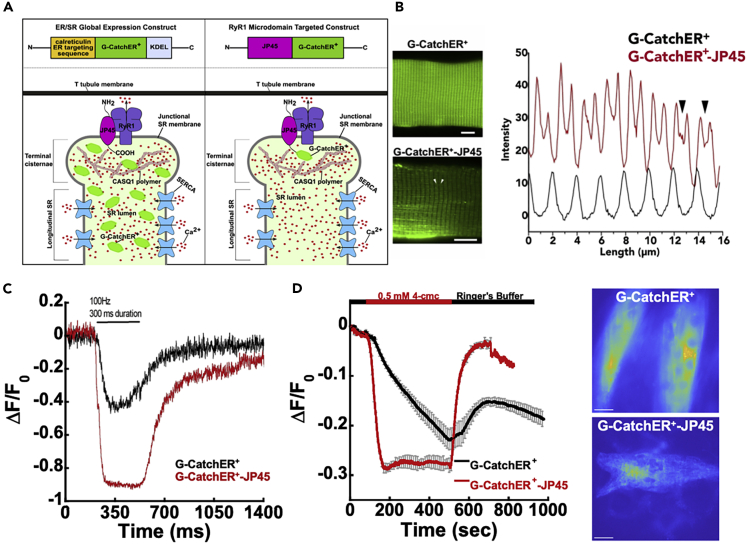
Figure 5.
Monitoring global and microdomain changes in SR Ca2+ with globally expressed and targeted G-CatchER+
(A) Representative plasmid construction and expression of globally expressed G-CatchER+ and targeted G-CatchER+-JP45 in the skeletal muscle SR. (Left panel) Global expression of G-CatchER+. G-CatchER+ contains the calreticulin signal peptide at the N terminus and the KDEL ER/SR retention sequence at the C-terminus. Resulting expression of the sensor follows a uniform distribution pattern throughout the SR monitoring global Ca2+. (Right panel) RyR1 microdomain targeted G-CatchER+ with JP45. G-CatchER+ resides at the C-terminus of JP45. Resulting expression of the sensor positions it near the lumenal opening of RyR1 in proximity to CASQ1 polymers that establish a large proximate Ca2+ pool in the TC necessary for E-C coupling.
(B) Wild-type FDB fibers were transfected with G-CatchER+ and G-CatchER+-JP45. Images reveal differential expression patterns for the targeted and un-targeted probe. Intensity changes from G-CatchER+ and G-CatchER+-JP45 fibers plotted against fiber length. Arrows correspond to arrows on G-CatchER+-JP45. A clear distinction is seen in the localization of G-CatchER+ and G-CatchER+-JP45.
(C) Ca2+ transients in FDB fibers were recorded upon stimulation with a 100-Hz electrical pulse for 300 ms. Black trace is fluorescence intensity monitored with G-CatchER+ expressed globally, and the red trace is G-CatchER+-JP45 located at the lumenal side of the junctional face membrane of the terminal cisternae.
(D) HILO imaging in C2C12 myotubule cells for G-CatchER+ (black, n = 6) and G-CatchER+-JP45 (red, n = 3) in response to 500-μM 4-cmc with representative cells for imaging. Scale bars, 10 μm in panel (B) and 20 μm in panel (D).
See also Figure S5.