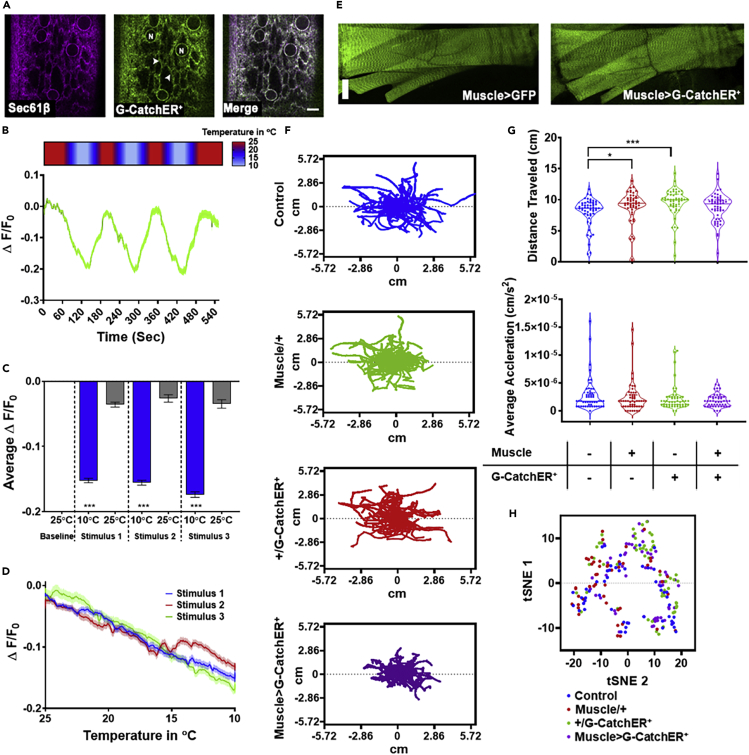
Figure 6.
In vivo G-CatchER+ validation in Drosophila melanogaster larval muscles
(A) In vivo validation of transgenic G-CatchER+ expression in muscle ER/SR. The ER translocon complex protein Sec61β tagged with tdTomato (left, magenta) and G-CatchER+ (middle, green) exhibit tight co-localization in larval muscle characterized by perinuclear (nucleus marked by “N”) and reticular network subcellular distributions (arrowheads). Genotype: Mef2>G-CatchER+, Sec61β::tdTomato. Scale bar, 10μm. Representative image from N = 10 larvae.
(B and C) Assessing cold-evoked ER/SR Ca2+ dynamics in muscle using G-CatchER+. Heatmap (B, top) shows stimulus temperature, where warmer temperatures are in red and cooler temperatures are in light blue. (B, bottom) Ca2+ levels reduce in response to cold stimulus, where percent change in fluorescence of G-CatchER+ plotted against time in seconds. Stimulus regimen details in the Methods. N = 20 animals. Error bars ±SEM. (C) Average percent change in fluorescence of G-CatchER+ at 25°C and 10°C, where there is a significant decrease in G-CatchER+ fluorescence at 10°C when compared with 25°C. Genotype: Mef2>G-CatchER+. N = 20 animals. Error bars ±SEM, ∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Kruskal-Wallis test.
(D) Analyses of G-CatchER+ sensor dynamics reveal temperature-dependent increases in Ca2+ release across the three cold ramp stimulations with the greatest change in fluorescence at the lowest temperature (10°C).
(E) Expression of G-CatchER+ does not grossly alter muscle morphology. (Left) Muscle cells expressing GFP and (right) muscle cells expressing G-CatchER+. Genotype: Mef2>GFP and Mef2>G-CatchER+. Scale bar, 50 μm. Representative image from N = 10 larvae.
(F–H) Drosophila larval locomotion assay to assess potential impacts of extended G-CatchER+ expression on larval crawling behavior. (F) Larval locomotion tracks for individual animals during 1-min assay across various genotypes. (G, top) Distance traveled in cm and (G, bottom) average acceleration in cm/s2. N = 48–52 animals; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Kruskal-Wallis test. (H) t-SNE analysis of multiple metrics including average distance traveled, average velocity, average acceleration, average bending, and total moving time. Iterations = 1000, perplexity = 20. (F–H) Genotype: Control (w1118), Muscle/+ (Mef2-GAL4 (x) w1118), +/G-CatchER+ (UAS-G-CatchER+ (x) w1118), and Muscle > G-CatchER+ (Mef2-GAL4 (x) UAS-G-CatchER+). N = 48–52 animals.