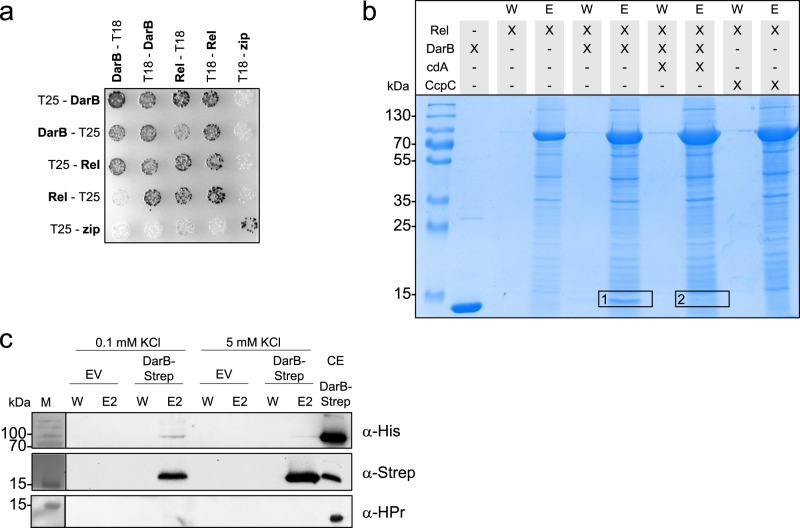
Fig. 1. DarB interacts with Rel in vitro and in vivo.
a Bacterial two-hybrid (BACTH) experiment testing for the interaction of DarB with Rel. N- and C-terminal fusions of DarB and Rel to the T18 or T25 domains of the adenylate cyclase (CyaA) were created and the proteins were tested for interaction in E. coli BTH101. Dark colonies indicate an interaction that results in adenylate cyclase activity and subsequent expression of the reporter β-galactosidase. The experiment was conducted three times and a representative plate is shown. b In vitro Strep-Rel pulldown experiment. Strep-Rel was immobilized onto a StrepTactin column and incubated with DarB, DarB preincubated with c-di-AMP, or the control protein CcpC. The eluates (E) and wash (W) fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and the presence of DarB in the elution fractions was further verified by MS analysis (excised gel bands are numbered with 1 and 2). The experiment was conducted three times and a representative gel is shown. c In vivo interaction experiment of DarB-Strep with Rel-His. B. subtilis expressing Rel-His6 was transformed with plasmid-borne DarB-Strep and grown in minimal medium containing low (0.1 mM) or high (5 mM) potassium concentration. DarB together with its potential binding partners was purified with a StrepTactin column and the elution and wash fractions were analyzed by western blot analysis. DarB and Rel were detected by using antibodies against the Strep-tag and the His-tag, respectively. HPr served as a negative control. EV, empty vector; CE, cell extract; cdA, c-di-AMP. The western blot was conducted three times and a representative gel is shown.