Figure 1.
Constellation-Seq methodology and performance
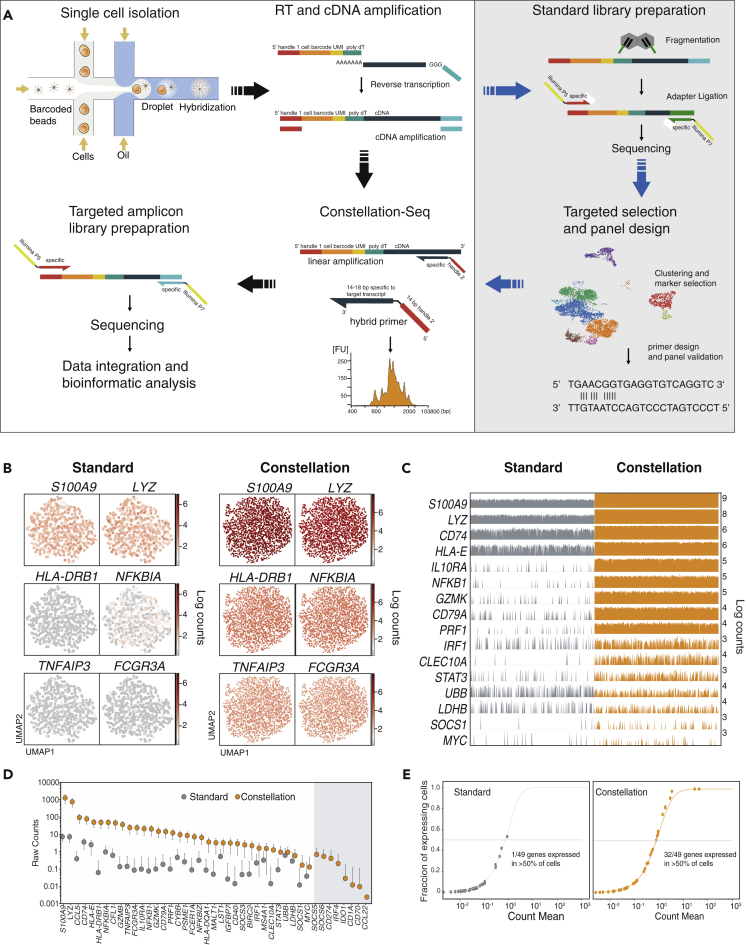
(A) Schematic representation of the method: Constellation-Seq can be applied to any Smart-Seq-like library following the standard cDNA synthesis protocol. With a defined primer panel, Constellation-Seq can be applied directly to the cDNA library (black arrows). Otherwise, an aliquot of the cDNA can be used for bulk sequencing and after data analysis the panel of primers can be selected for hypothesis testing or to reduce the technical zeros (Blue arrows). Constellation-Seq includes a hybrid primer (14–18 bp specific sequence, black, adjacent to a common 14 bp handle 2, red) that binds to a specific target sequence in the cDNA library. Linear amplification of 500–1000 bp stretches of target transcripts allows selective enrichment of targets of interest, and the inclusion of the cell barcode and UMI sequences, leads to generation of the Constellation library, ready to use in next-generation sequencing. (B-E) Constellation-Seq was compared against standard sequencing using a panel of 52 targets on control beads.
(B) UMAP representation of control beads with standard sequencing compared with Constellation-Seq.
(C) A track plot showing the reduction in the data sparsity in a head to head comparison. Each bar represents a gene expression signal from a single cell. A full track plot is included as Figure S4.
(D) Individual target raw counts show ~100-fold sensitivity gains for Constellation-Seq, error bars represent SD.
(E) Dramatic reduction in technical zeros achieved by Constellation-Seq compared with DropSeq. At 2K UMI counts per bead 32/49 genes were detected in half of the beads (3 negative controls were not detected) using Constellation-Seq, whereas only 1 was detected with the same threshold using DropSeq.