FIGURE 1.
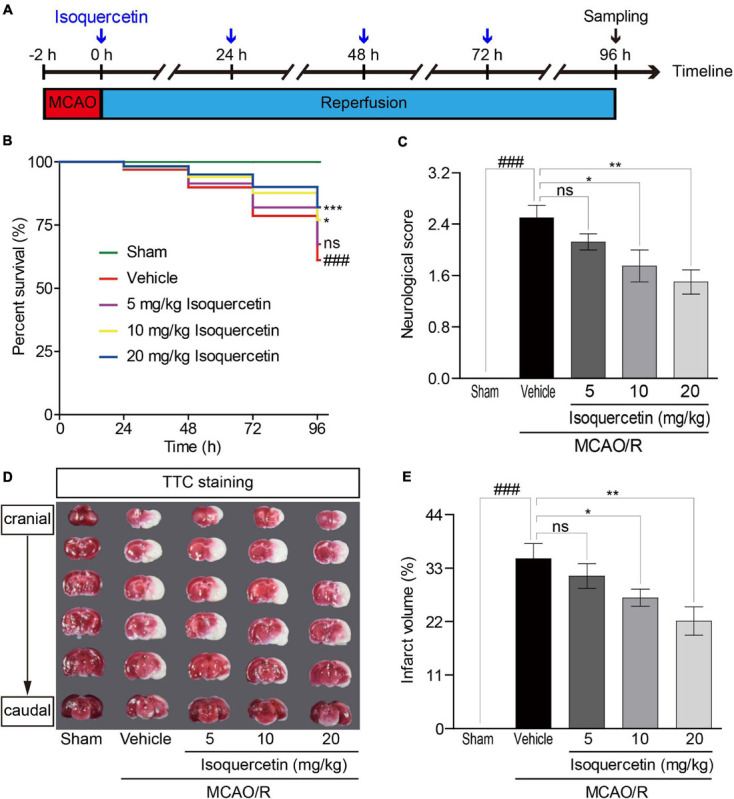
Effects of isoquercetin on brain injury in MCAO/R-induced rats. Isoquercetin (5, 10, and 20 mg/kg/day) was orally administered after 2 h MCAO for four consecutive days. (A) Scheme of the animal experimental protocol. (B) The survival percentage of rats after MCAO/R and isoquercetin treatments (n = 45). (C) Neurological deficit scores after MCAO/R and oral administration of different doses of isoquercetin (n = 6). (D) Representative coronal brain sections (2 mm-thick, measured in six serial coronal sections arranged from cranial to caudal regions) from sham-operated, vehicle-treated, or isoquercetin-treated rats stained with 2% TTC staining. Red colored regions in the TTC-stained sections are non-ischemic regions, and pale-colored regions indicate the ischemic portions of the brain. (E) Quantitative analyses of infarct volumes. The infarct volumes from sham groups were all equal to zero. The influence of edema on infarct volume was corrected by standard methods (volume of contralateral hemisphere – volume of non-ischemic ipsilateral hemisphere), with infarcted volume expressed as a percentage of the contralateral hemisphere (n = 6). Results were present in mean values ± SEM. ###p < 0.001 vs. sham group; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 vs. vehicle-treated group.
