Figure 1.
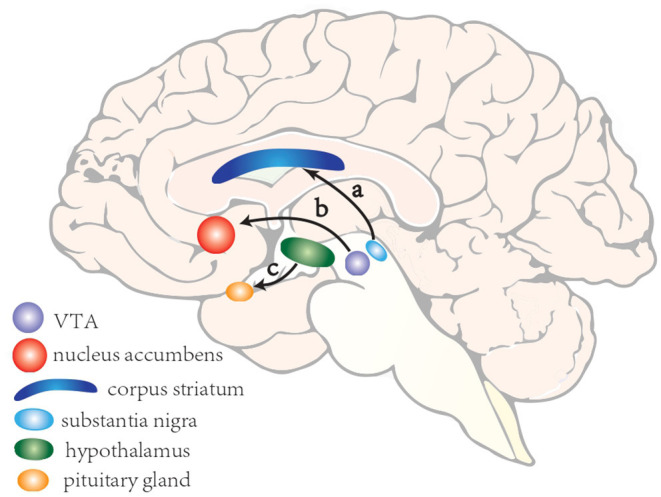
A schematic illustration of three main dopaminergic pathways in central nervous systems. (a) the nigrostriatal pathway consisting of cell bodies in the substantia nigra whose axons terminate in the corpus striatum; (b) the mesocorticolimbic pathway (also known as the reward system), whose cell bodies are situated in the ventral tegmental area and whose axons project to parts of the limbic system; and (c) the tuberoinfundibular pathway, whose cell bodies are found in the ventral hypothalamus and project to the median eminence and pituitary gland.
