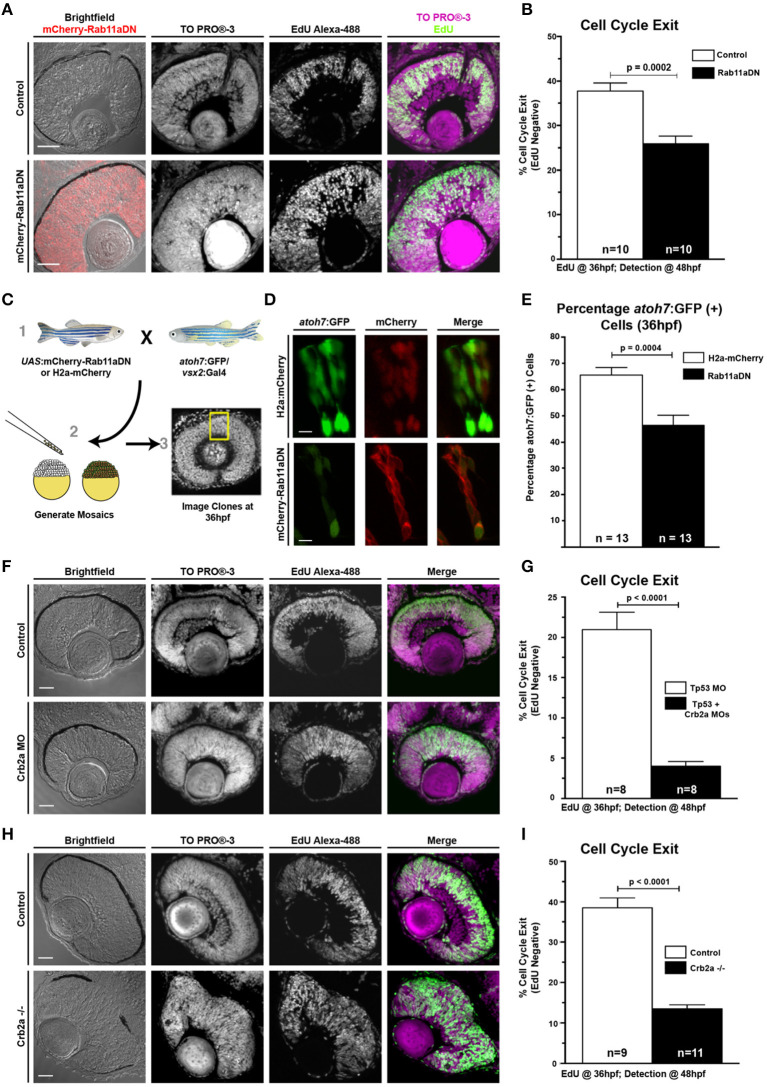
Figure 3.
Rab11aDN expression and Crb2a loss-of-function promote RPC proliferation. (A) Representative retinal sections of Control (top) and Rab11aDN (bottom) retinas assessing RPC proliferation through detection of EdU incorporation at 48 hpf after a 12 h pulse from 36 to 48 hpf with nuclei counterstained with ToPRO-3. (B) Quantification of retinal cell cycle exit in Control and Rab11aDN EdU experiments. (C) Experimental design for assessing retinal neurogenesis in Rab11aDN genetic mosaics using the atoh7:GFP neurogenic reporter. (D) Representative images of Control (top) and Rab11aDN (bottom) genetic mosaics assessing retinal neurogenesis (atoh7:GFP). (E) Quantification of percentages of neurogenic cells (atoh7:GFP) in genetic mosaic experiments. Listed n's represent total number of clones assayed across >10 embryos/genotype. (F,H) Representative retinal sections of (F) Crb2a morphant or (H) Crb2a mutant retinas assessing RPC proliferation through detection of EdU incorporation at 48 hpf after a 12 h pulse from 36 to 48 hpf with nuclei counterstained with ToPRO-3. (G,I) Quantification of retinal cell cycle exit comparing Control and either (G) Crb2a morphant or (I) Crb2a mutant embryos. N's in (G,I) represent number of centrally localized retinal sections quantified, with 1 section counted/animal. Bar graphs in (B,G,I) represent mean with error bars indicating SEM. Statistics are the results of an unpaired t-test. Scale bars in (A,C,F) represent 50 μm, with the scale bars in (D) representing 15 μm.