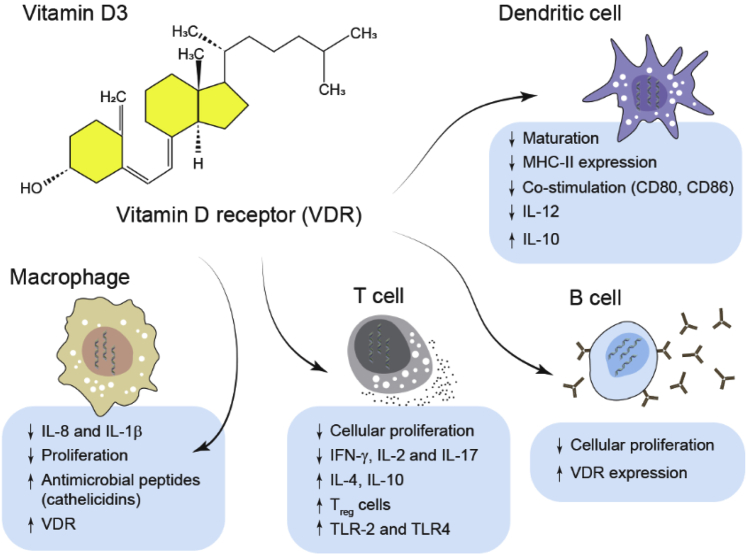
Figure 2.
Effects of vitamin D on the immune system: Vitamin D (Vit D) is a fat-soluble vitamin and the main functional isoform is Vit D3. Passive diffusion is the main mechanism by which immune system cells acquire Vit D3. Post entry, Vit D3 binds to its nuclear receptor, Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) where it has a broad modulatory activity on immune system cells. Treatment with Vit D3 increases the host cell ability to express TLR-2 and TLR-4 leading to an increase in antimicrobial peptide expression (cathelicidins). Furthermore, it exerts antiinflammatory effects by downregulating macrophage and dendritic cell activity (decrease IL-8 and IL-1β expression) as well as T cell activation (increased IL-10 and decrease in IFN-γ, IL-2 and IL-17 expression) and an increase in Treg cells (regulatory activity). Abbreviations: IL, interleukin; TLR, Toll-like receptor.