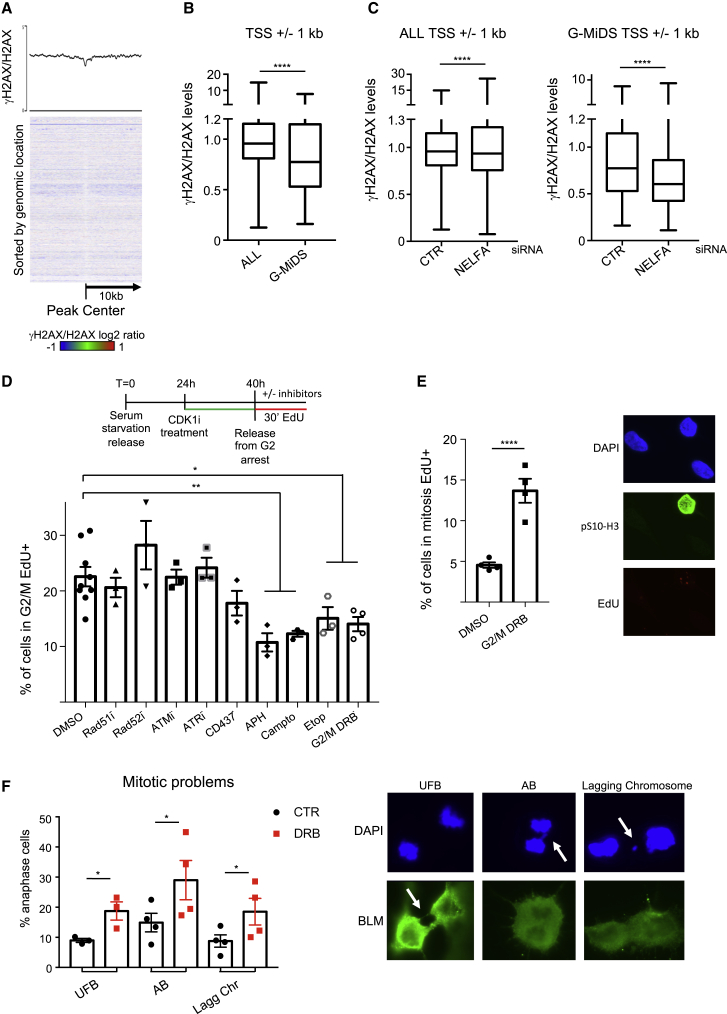
Figure 6.
G-MiDS is not dependent on the DNA damage response and is distinct from MiDAS
(A) Average metagene profile and heatmap for γH2AX/H2AX at G-MiDS-specific peaks ±10 kb.
(B) Quantification of γH2AX/H2AX levels around TSSs ±1 kb of all transcribed genes and G-MiDS hotspots.
(C) Quantification of γH2AX/H2AX levels around TSSs ±1 kb of all transcribed genes and G-MiDS hotspots in CTR cells and after KD of NELFA.
(D) G2/M-EdU double-positive cells quantified in CTR DMSO cells or with the inhibitors (Rad51i = 25 μM, Rad52i = 20 μM, ATMi = 10 μM, ATRi = 4 μM, CD437 = 5 μM, aphidicolin [APH] = 10 μM, camptothecin [Campto] = 1 μM, and etoposide [Eto] = 10 μM) for 30 min once released from G2 arrest; DRB (100 μM) treated for 1 h before and then 30 min once released from G2 arrest; n ≥ 3.
(E) Immunofluorescence for pS10-H3 (green) to label mitotic cells, EdU Click-iT for DNA synthesis (red), and DAPI (blue) for nuclei staining. Only mitotic-EdU double-positive cells from prometaphase on were quantified; cells were treated with DMSO or DRB as in (D); n = 4.
(F) Immunofluorescence for Bloom (BLM; green) and DAPI (blue) for nuclei staining in cells released after the Ro3306 G2 arrest for 80 min in DMSO or DRB (100 μM), quantifying ultrafine bridges (UFB), anaphase bridges (AB), and lagging chromosomes (Lagg Chr), with examples highlighted by white arrows; n ≥ 3. Data represent mean ± SEM; Student’s t test; ns, not significant; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.