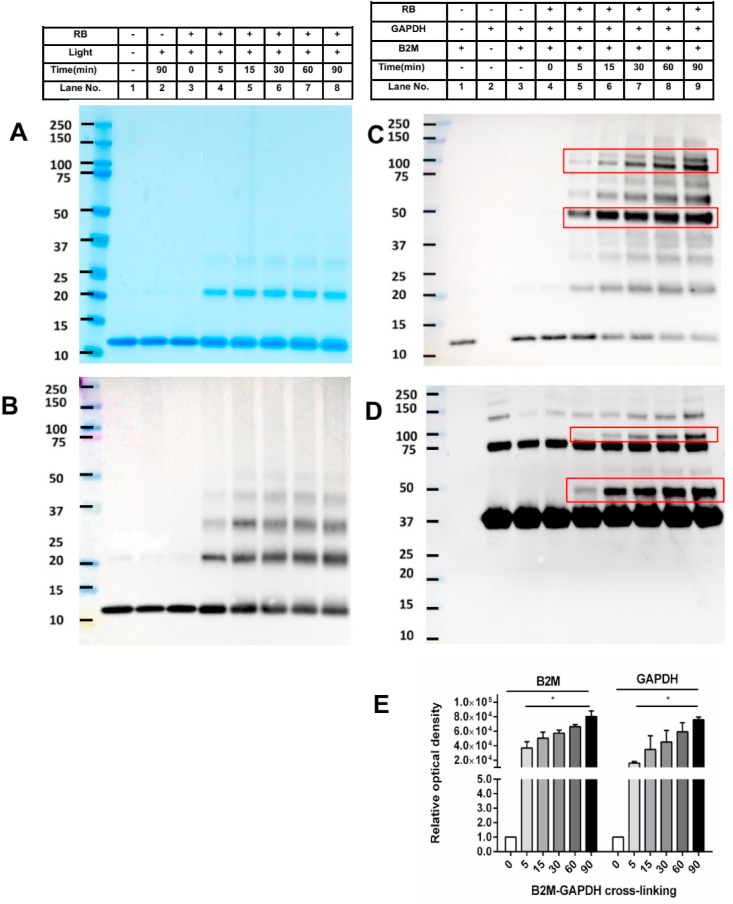
Fig. 1.
Detection of 1O2-induced B2M aggregation and formation of B2M-GAPDH cross-links. Panel A: representative image of B2M (20 μM in 10 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.4) subjected to increasing periods of illumination in the absence or presence of Rose Bengal/visible light and O2 (as indicated), with subsequent separation by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining. Panel B: As panel A, but with subsequent transfer of the proteins separated by SDS-PAGE to a PVDF membrane and probing with an anti-B2M antibody. Panel C: representative immunoblot image of B2M-GAPDH cross-link detection upon exposure of B2M to 1O2 for different time points, subsequent reaction with GAPDH, separation by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using anti-B2M antibody. Panel D: As panel C, but with detection using an anti-GAPDH antibody. Panel E: Optical density ratio (OD n min/OD 0 min) of B2M-GAPDH cross-linking bands from immunoblotting data in panels C, D (n = 0 min, 5 min, 15 min, 30 min, 60 min and 90 min). Each gel image or blot is representative of one of three, obtained from three independent experiments. Quantitative data are presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Statistical differences were examined using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett's multiple comparison test and are indicated as follows: *P < 0.05 treatment vs. lane 4 in panels C, D.