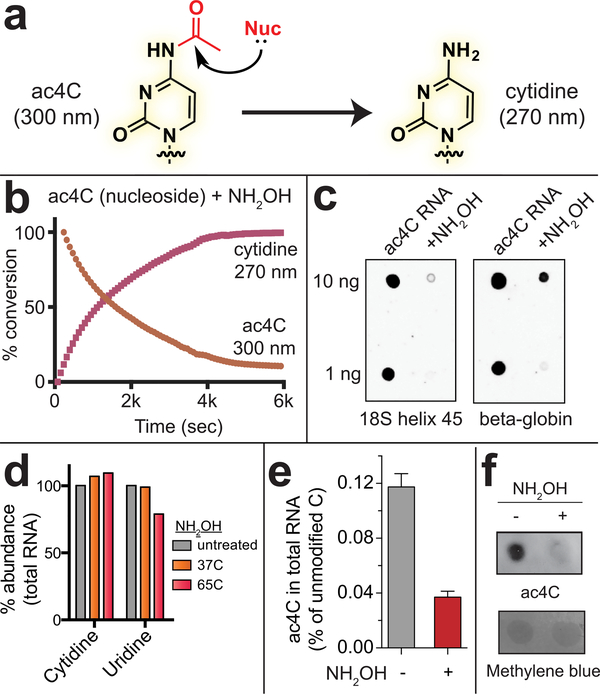
Figure 4.
Profiling ac4C using its specific reactivity. (a) Scheme for chemical deacetylation of ac4C. (b) Effect of hydroxylamine on ac4C free nucleoside monitored by UV spectroscopy. Reaction conditions: 0.25 mM ac4C [free nucleoside], 50 mM hydroxylamine, Tris at pH 7.0. (c) Effect of hydroxylamine on ac4C in RNA monitored by anti-ac4C dot blot. Reaction conditions: 50 mM hydroxylamine, Tris at pH 8.0, 65 °C, 1 h. (d) Effect of hydroxylamine (50 mM, pH 7.0) on overall cytidine and uridine base content in total RNA analyzed by HPLC. (e) Effect of hydroxylamine (50 mM, pH 7.0, 65 °C, 1 h) on ac4C in total cellular RNA analyzed by LC-MS/MS. (f) Anti-ac4C antibody can detect chemical ablation of ac4C in total cellular RNA.