Figure 2.
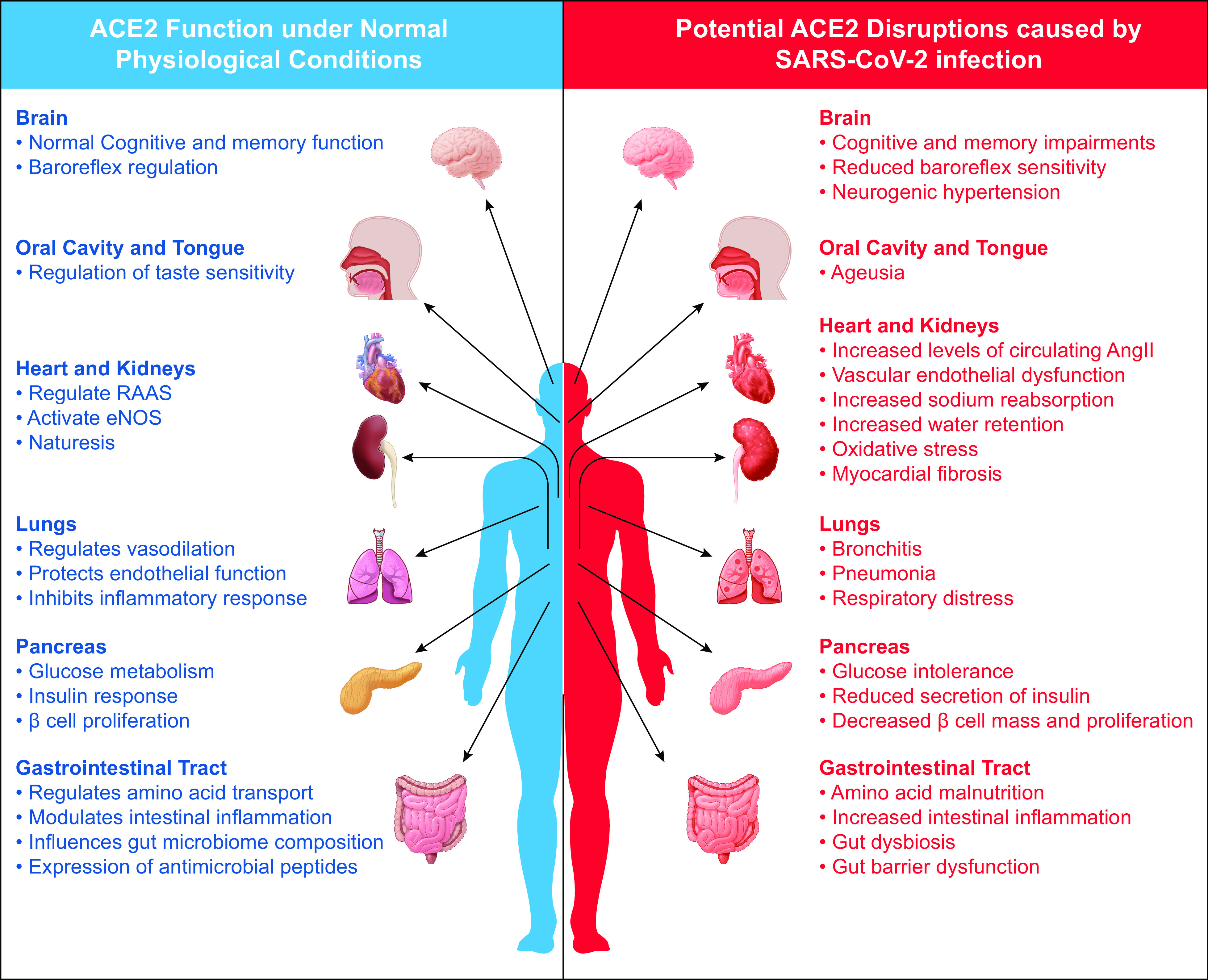
An organ review of normal ACE2 function versus potential pathophysiological consequences of ACE2 disruption caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection. ACE2 is present in various tissues, and its expression is vital to normal physiological functions. ACE2 disruption initiated through the binding of SARS-CoV-2 may have short- and long-term pathophysiological consequences to numerous organ systems that utilize ACE2 for proper function. ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2.
