Figure 4.
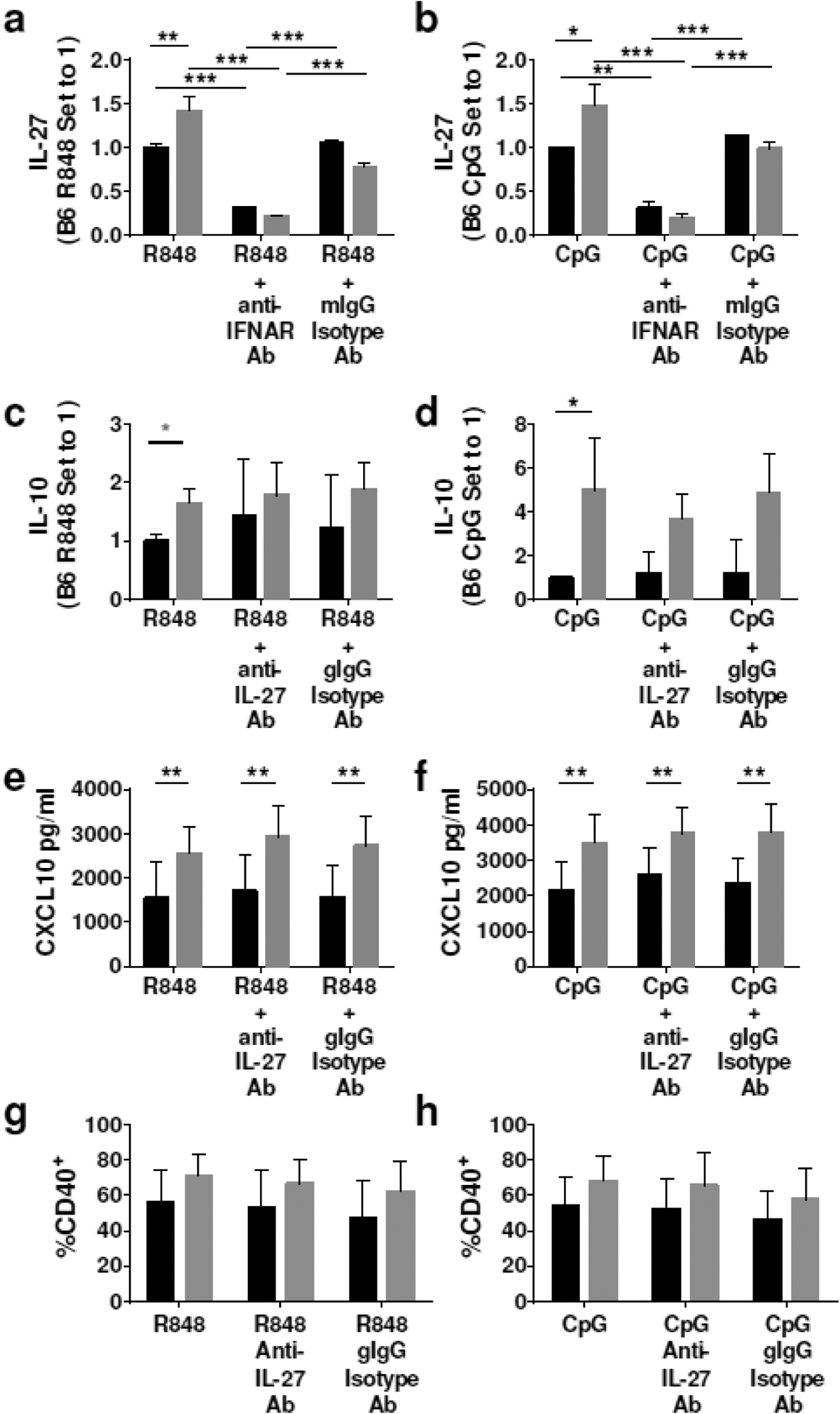
IFNAR blockade prevents IL-27 production in cDCs. (a-b) cDCs were treated with anti-IFNAR antibody (10 μg/ml) or mouse IgG isotype control (10 μg/ml) for 1 hour prior to stimulation with R848 (1 μg/ml) and CpG (10 μg/ml) for 24 hours. (c-h) cDCs were treated with anti-IL-27 antibody (1 μg/ml) or goat IgG isotype control (1 μg/ml) for 1 hour prior to stimulation with R848 (1 μg/ml) and CpG (10 μg/ml) for 24 hours. (a-b) IL-27 was measured by IL-27 ELISA Ready-Set-Go!™ Kit in the supernatants collected 24 hours after TLR stimulation. (c-d) IL-10 was measured by ELISA in the supernatants collected 24 hours after TLR stimulation. (e-f) Supernatants were collected 24 hours after stimulation and CXCL10 was measured by ELISA. (g-h) cDCs were collected at 24 hours after stimulation and stained. Samples were gated on singlets, scatter gate, live cells, CD11c+ CD11b+, CD40+. Dotted lines represent PBS treated B6 (20.6%) or TCSle (22.7%) CD40 expression (a-e) Results show an average and SE of 4–6 replicates from 3 experiments. (a-d) Due to inter-experimental variation, B6 stimulation condition is set to 1. Statistical significance was calculated by ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison test with the exception of (c) gray star representing statistical significance calculated by unpaired t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ns means not significant.
