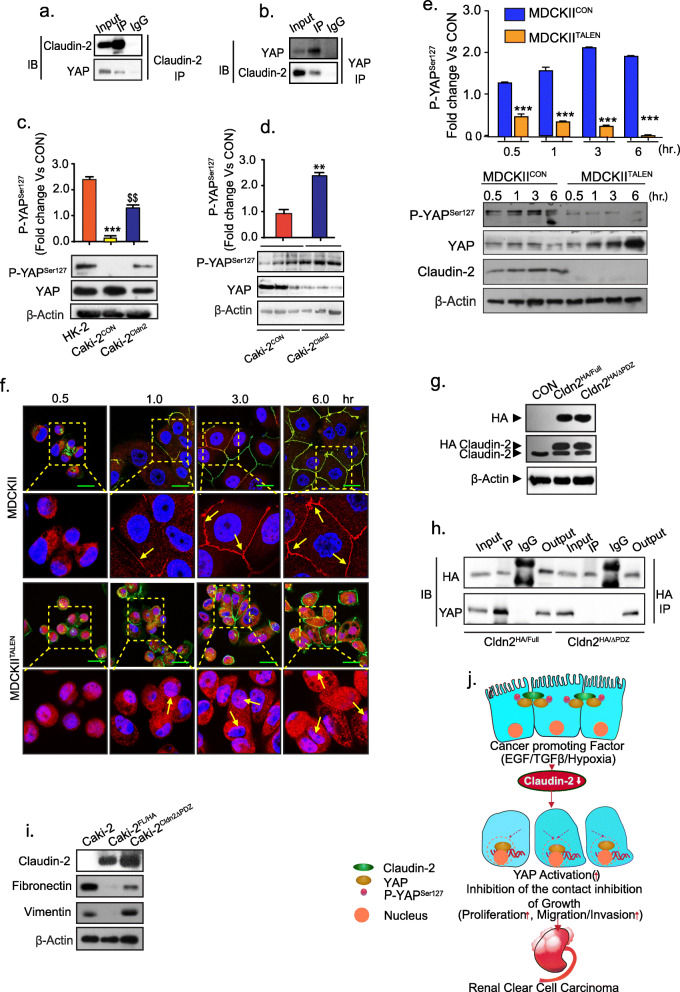
Fig. 6.
Claudin-2 interacts with YAP through its PDZ binding motif and hinders its nuclear localization and activation. a Total cell lysate from MDCK-II cells was subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-claudin-2 antibody and then immunoblotted with anti-YAP; (b) Total cell lysate from MDCK-II cells was subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-YAP antibody and immunoblotting with anti-claudin-2 or anti-YAP antibody; (c) Immunoblotting of p-YAPS127/YAP and its densitometry analysis; (d) Immunoblot analysis and quantitation of p-YAPS127/YAP using the total tissue lysates from Caki-2CON and Caki-2Cldn2 cell induced (xenograft) tumors; (e) Representative immunoblot analysis of p-YAPS127, YAP and claudin-2 expression using total cell lysate from MDCKII and MDCKIITALEN cells subjected to a time-course of growth, and densitometric quantitation of p-YAPS127; (f) Immunofluorescent analysis of YAP and ZO-1 proteins in MDCKII and MDCKIITALEN cells growing in time dependent manner (30 min to 6 h). Yellow box area from MDCKII cells and MDCKIITALEN cells was enlarged below to show YAP localization. Arrows indicate localization of the YAP protein; (g) Immunoblot analysis of MDCK-II cell lysate expressing claudin-2-HA recombinant protein (expressing Cldn2FL/HA plasmid) or claudin-2 protein lacking the PDZ-binding motif (expressing Cldn2ΔPDZ/HA plasmid); (h) Immunoprecipitation using anti-HA antibody. Total cell lysate of MDCK-II cell expressing Cldn2FL/HA plasmid construct and Cldn2ΔPDZ/HA construct was used for immunoprecipitation and subsequently immunoblotted with anti-HA or anti-YAP antibody; (i) Representative Immunoblots of EMT marker in Caki-2 cells transfected with Cldn2FL/HA or Cldn2ΔPDZ/HA expression construct; (j) Graphical modelling of the overall concept. Differentiated PTE cell having apical claudin-2 (green) which interacts with YAP (brown) protein and sequestered to membrane. Cancer promoting factors induce down-regulation of claudin-2 expression. Loss of claudin-2, in turn, promotes loss of cell-cell contact and de-localization of YAP protein to the cell nucleus and hence induction of proliferation and RCC progression. Data is presented as mean + sem. Statistical significance was determined by student t test and 1-way ANOVA and post hoc Tukey’s test for pairwise comparison. ** or $$ P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001