Fig. 8. n-APLP1 and n-CHL1 are correlated with phosphorylated Tau in the CSF of healthy controls and patients with AD.
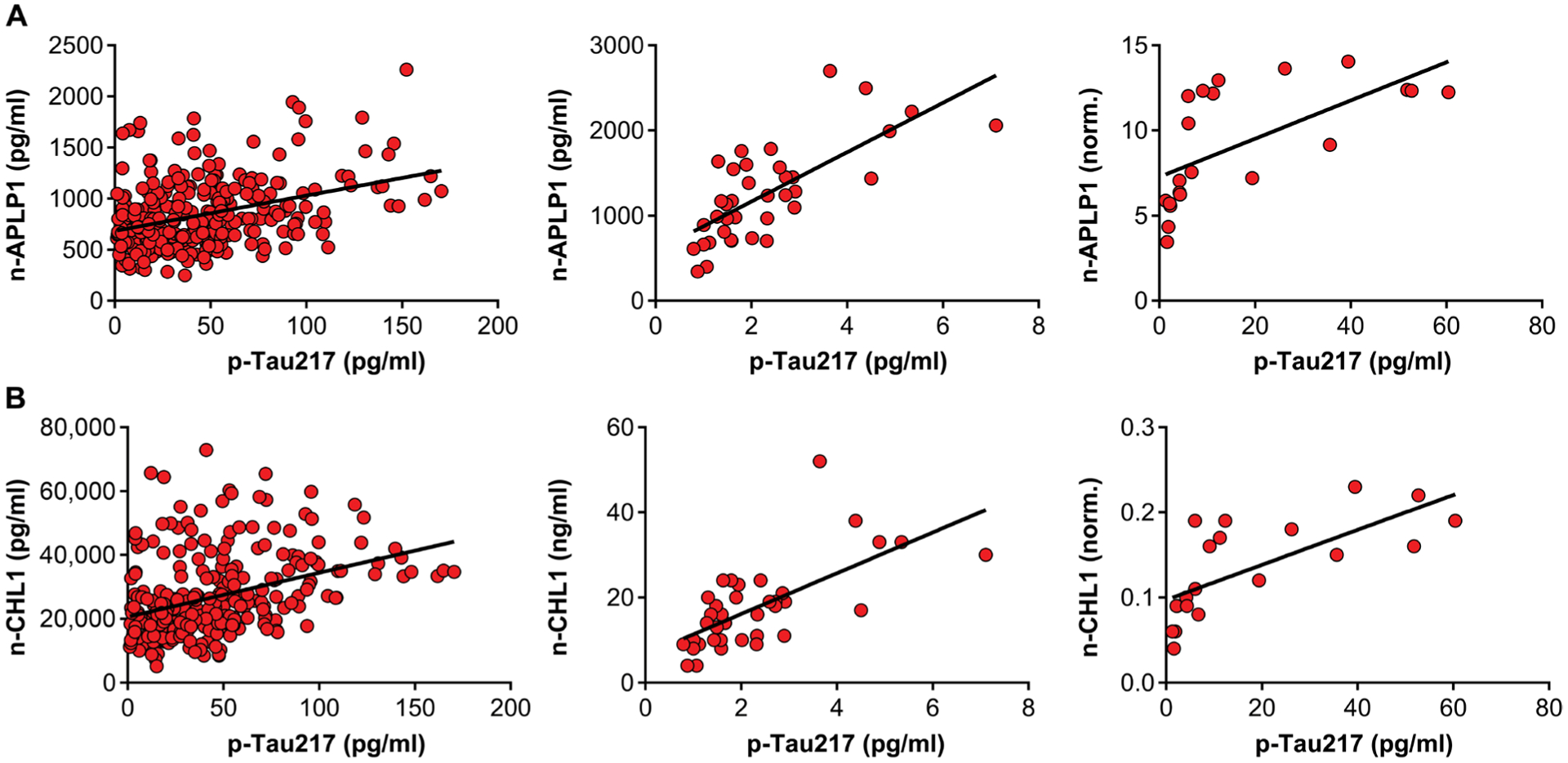
(A) Scatterplots showing the relationship between n-APLP1 and p-tau217 in the CSF of patients with mild to moderate AD (left; n = 316; β = 0.36, P = 6.5 × 10−11), healthy controls (middle; n = 37; β = 0.72, P = 5.1 × 10−7), and MCIs adjusted for CSF Aβ42 (right; n = 21; β = 0.63, P = 0.002). (B) Scatterplots showing relationship between n-CHL1 and p-tau217 in the CSF of patients with mild to moderate AD (left; n = 316; β = 0.37, P = 6.4 × 10−11), healthy controls (middle; n = 37; β = 0.62, P = 5.0 × 10−6), and MCIs adjusted for CSF Aβ42 (right; n = 21; β = 0.71, P = 0.0003).
