Figure 1.
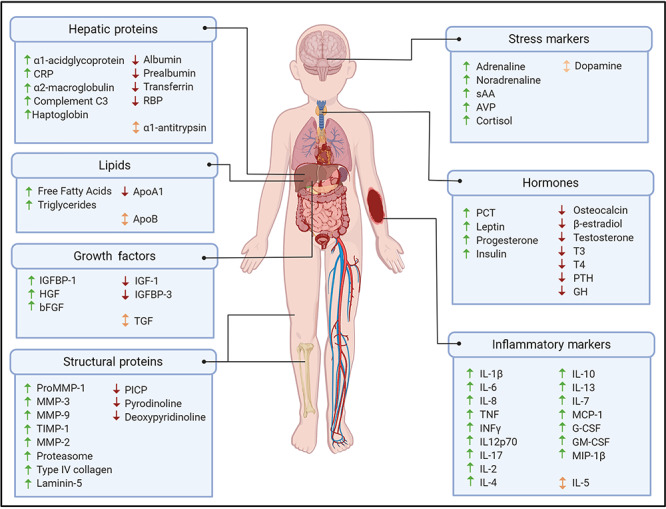
Summary of reported systemic biomarker changes in response to paediatric burn injury. Up arrows (↑) indicate increased abundance of biomarker following a burn in children; down arrows (↓) indicate reduced abundance of biomarker following a burn in children; and bidirectional arrows (↕) indicate conflicting evidence for biomarker abundance following a burn in children. Image created with BioRender.com. CRP C-reactive protein, RBP retinol binding protein, sAA salivary alpha-amylase, AVP arginine vasopressin, IGF insulin-like growth factor, IGFBP insulin-like growth factor binding protein, HGF hepatocyte growth factor, bFGF basic fibroblast growth factor, TGF transforming growth factor, PCT procalcitonin, T3 triiodothyronine, T4 thyroxine, PTH parathyroid hormone, GH growth hormone, MMP matrix metalloproteases, PICP carboxyterminal propeptide of type I procollagen, TIMP-1 tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1, IL interleukin, TNF tumour necrosis factor, INFγ interferon-gamma, MCP-1 monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, G-CSF granulocyte-colony stimulating factor, GM-CSF granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, MIP-1β macrophage inflammatory protein 1β
