Figure 4.
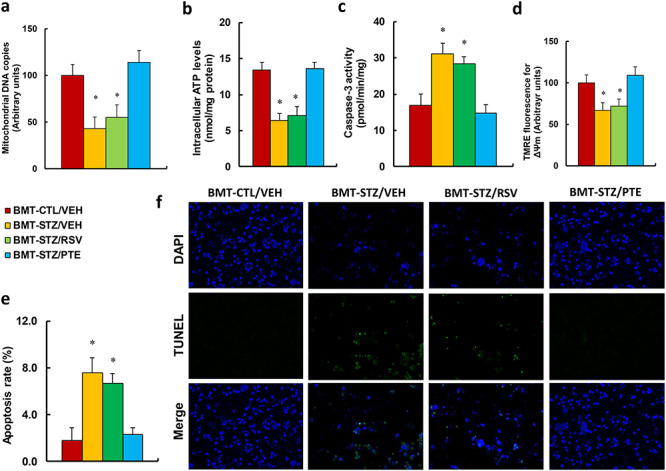
BMT of PTE-treated diabetic HSCs protects against diabetes-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in PBMCs. Experimental rats were randomly separated into 4 groups as follows: rats with BMT of HSCs from CTL/VEH (BMT-CTL/VEH); rats with BMT of HSCs from STZ/VEH (BMT-STZ/VEH); rats with BMT of HSCs from STZ/RSV (BMT-STZ/RSV); and rats with BMT of HSCs from STZ/PTE (BMT-STZ/PTE). The rats were subjected to a model of cutaneous burn injury and the PBMCs were collected for biomedical analysis after a 3-week period post-burn. (a) mDNA copies, n = 4; (b) the intracellular ATP level, n = 4. (c) Caspase-3 activity, n = 5. (d) ∆ᴪm by TMRE fluorescence, n = 5. (e) Apoptosis rate by TUNEL assay, n = 5. (f) Representative pictures for (e). For bars in graphs marked with an asterisk, p < 0.05 vs BMT-CTL/VEH group. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. BMT bone marrow transplantation, PTE pterostilbene, HSCs hematopoietic stem cells, PBMCs peripheral blood mononuclear cells, CTL control, VEH vehicle, STZ streptozotocin, RSV resveratrol, ATP Adenosine triphosphate, TMRE tetramethyl rhodamine ethyl ester, TUNEL terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling
