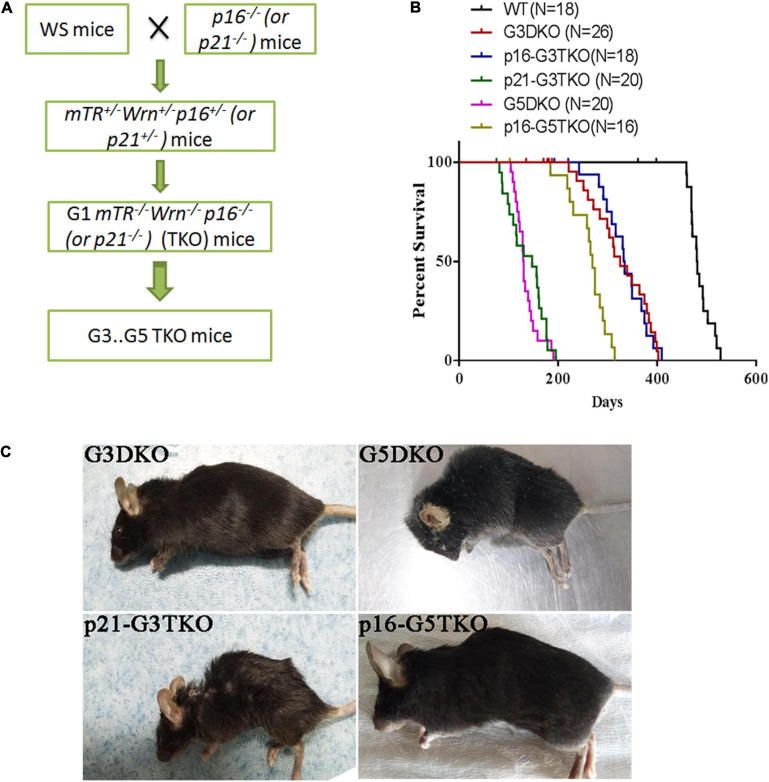
FIGURE 1.
The generation and lifespan of p16/p21-TKO mice. (A) The breeding strategy for generating p16/p21TKO mice. The p16– /– or p21– /– mice were crossed with WS mice and G1TKO (G1mTR– /– Wrn– /– p21– /– or G1mTR– /– Wrn– /– p16– /– ) mice were obtained. Then, the mice were bred generation by generation to obtain G2, G3, G4, G5 TKO mice. (B) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of G3DKO, p16-G3TKO, p21-G3TKO, G5DKO, and p16-G5TKO mice. For G3DKO, p21 deficiency shortened the lifespan (p < 0.001), while p16 deficiency slightly increased the lifespan (p = 0.0018). For G5DKO, p16 deficiency dramatically prolonged the lifespan (p < 0.001). Because an accelerated aging phenotype occurred in p21-TKO, mice with this genotype could only be bred to G3TKO. (C) The mouse appearance and body size also showed that p21 deficiency accelerated the aging phenotypes of WS, while p16 deficiency rescued it.