Abstract
Background
The dietary landscape has changed rapidly in China in the past few decades. This research investigates the associations of older adults’ choices and consumption of staple foods and cooking oils with obesity-related measurements.
Methods
Panel data were extracted from the Chinese Longitudinal Health Longevity Survey from 3253 older participants with 6506 observations. Ordinary least squares and ordered logistic regression models were estimated with the outcomes of obesity determined by waist circumference (WC) and body mass index (BMI), respectively.
Results
Older men who consumed wheat had wider WCs (β=2.84 [95% confidence interval {CI} 1.55 to 4.13], p<0.01) and higher BMIs (adjusted odds ratio 1.74 [95% CI 1.40 to 2.17], p<0.01) than those who preferred rice. Female participants who used animal-based cooking oil had lower WCs and BMIs than their counterparts who consumed vegetable-based cooking oil. Increased consumption of staple foods was associated with increased rates of obesity in both sexes.
Conclusion
Dieticians and nutritionists should design appropriate dietary plans to help reduce obesity and chronic diseases among older Chinese adults. Further clinical trials are needed to continue investigating this topic.
Keywords: China, cooking oil, dietary shift, obesity, older adults, staple food
Introduction
The health threats of obesity are not limited to only Western industrialized countries. Obesity is rapidly becoming one of the key public health challenges in China. When it comes to unhealthy eating habits among the Chinese, it may appear that the problem is observed only in younger generations as the result of rapid Westernization which brought with it a culture of fast food and sweetened beverages.1 However, poor dietary habits also plague older generations in China. Around 50% of the elderly population reported consuming salt and oil excessively.2 A shift towards a more westernized diet (dairy, fruits, cakes and fast food) has also been observed and associated with increased body mass index (BMI).3
China is projected to have 115 million people >80 y of age by the year 2050.4 The increasing incidence of obesity among the aging population of China is a worrying phenomenon. In 2013, of the 202 million older adults in China, >100 million suffered from chronic diseases,5 with hypertension and diabetes being the two leading obesity-related conditions. However, those numbers may be underestimates, as many older adults have not been diagnosed due to the lack of a proper medical surveillance system in China.6 Some of those chronic diseases also predispose individuals to mental health disorders. For example, type 2 diabetes patients are more likely to suffer from depression and anxiety disorders in various regions in China.7
To preserve the physical and mental health of older adults, it is pertinent to promote healthy eating habits. Rice and vegetable oils are key components of a Chinese diet and are considered to be healthy foods if consumed in moderation. However, the high intake of white rice is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes,8 while the excessive consumption of vegetable oils is related to elevated blood pressure and cholesterol.9 In addition, a study of Chinese nonagenarians and centenarians found an association between poor nutritional status and cognitive impairment.10
Although previous papers have examined the associations between dietary patterns and obesity among older adults in China,2,3 little discussion has focused on the effects of staple foods and cooking oils, which are the essential ingredients of a Chinese diet, on the incidence of obesity among older adults in China. This research focuses on older adults, including the oldest old—octogenarians and nonagenarians. Currently, nutritional findings in those populations remain scanty but are nonetheless very important in the context of a rapidly aging population in China. A panel analysis is the main statistical method used in this study. In contrast to traditional cross-sectional approaches, the panel analysis enables researchers to evaluate dietary changes over time while accounting for intra-individual variability.11 Such a methodological approach should lead to more reliable research outcomes.
We hypothesized that the choice of staple foods and cooking oils by older adults is associated with obesity-related tendencies in China. Findings of this study would allow stakeholders to reassess the quality of public health efforts and dietary advice in China, especially among older adults, where there is the greatest need.
Methods
This research relies on panel data from the Chinese Longitudinal Healthy Longevity Survey (CLHLS). The CLHLS dataset was established by the Centre for the Study of Aging and Human Development (Duke University, Durham, NC, USA) with the support of numerous international collaborators such as the China Social Sciences Foundation, the Max Plank Institute for Demographic Research and the China Natural Sciences Foundation. The baseline survey started in 1998, with each wave of new surveys following every 2–3 y. By the 2014 cycle, the surveyed regions covered nearly 85% of the Chinese population (approximately 1.1 billion people). The CLHLS covered a wide spectrum of health-related measurements and behaviours in older adults. The measurements included substance use (smoking and alcohol use behaviours), social policy, health service utilization, social support, family relationships, disease diagnosis, self-reported dietary intake frequency and many other related variables. If an older adult was unable to participate in the CLHLS on their own, a close relative or a caregiver was asked to complete the survey. Informed consent was obtained from all research participants prior to the data collection. The data used in this study have been made available on a publicly accessible data-sharing domain without any personal information. Hence this research is exempted from institutional review board review.
The present study sample consists of older adults, ≥60 y of age, who answered all questions of interest in two waves of the CLHLS (2011–2012 and 2014). Participants who answered only one of the two surveys or who had missing information were excluded from the analyses. In addition, we excluded individuals who were bedridden. The final sample consisted of 1551 male and 1702 female participants (N=3253) with a total of 6506 records—two per participant. Figure 1 shows the procedure of sample selection.
Figure 1.
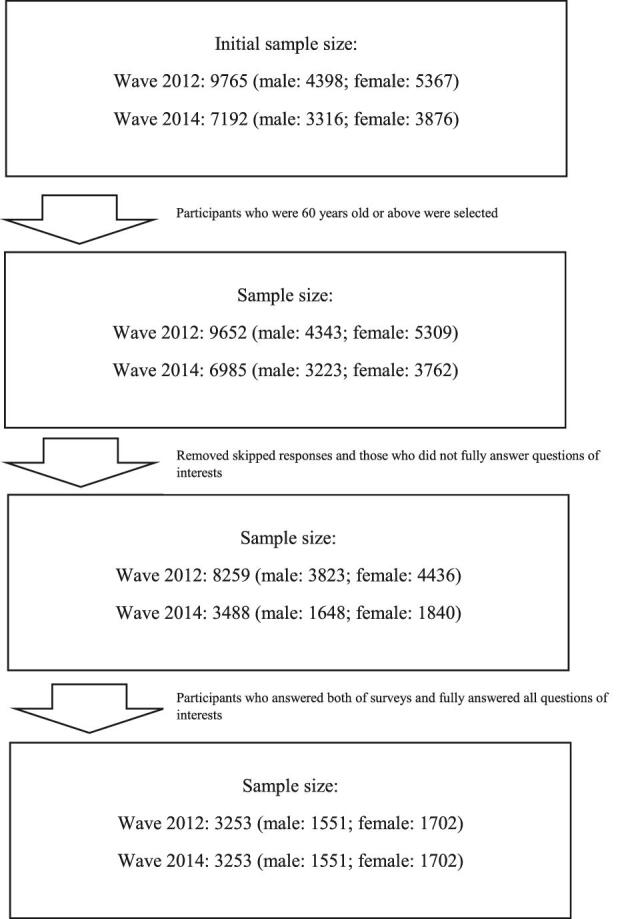
Process of sample selection.
This study is focused primarily on examining the associations of different types of staple foods and cooking oils with obesity. The five categories of staple foods included rice, corn (such as maize), wheat (such as noodles and bread products), half rice and half wheat and others. Daily quantities of each of these staple foods were measured in liang (Chinese unit of weight where 1 liang is approximately 50 g) and classified into three categories: 1–5 liang, 6–10 liang and >11 liang. ‘Types of cooking oils’ is a dichotomous variable, either vegetable/gingili (vegetable-based) or lard/animal fat (animal-based). Categories of cooking oils with similar characteristics were combined. Food-related measurements were self-reported by the CLHLS participants.
Besides these types of staple foods and cooking oils, three other food categories—fresh vegetables, fruits and meat—were included in all models. The frequency of consumption for fresh fruits and vegetables was stratified into daily, quite often, occasionally and rarely or none, while that for meat was daily, weekly, monthly, occasionally and rarely or none.
The assessment of obesity is based on waist circumference (WC) and body mass index (BMI), both of which are continuous variables. WC is preferred over BMI, as it is a relatively more accurate measurement of overall obesity status among older adults.12 WC was measured in centimetres while BMI was derived from the person's weight (in kilograms) divided by height (in meters) squared. For BMI, we classified this measurement into three categories: underweight (BMI<18.5), normal (BMI ≥18.5–<25) and overweight/obese (BMI≥25). Categorized BMI was considered an ordinal variable, but WC was kept in its original continuous form. Trained interviewers assessed these anthropometric measurements according to the standard protocol.
Besides the main predictors of consumption of various types of staple foods and cooking oils, we included the following demographics as covariates: age (60–80, 81–95 and >95), marital status (married, not married), household income (income quintiles with a ‘do not know the income’ category), years of formal education (none, 1–5, 6–11 and >11), types of community (urban, rural) and region of province (north, northeast, east, centre/south and west). In addition, we considered the participants’ physical activity (yes, no), comorbidities measured as the number of times suffering from chronic diseases in the past 2 y (0, 1–2 and >2) and general daily life measured as self-rated life satisfaction (good, neutral, bad and not able to answer).
Two different types of regression analysis were conducted. First, panel ordinary least squares (OLS) regression models were chosen to investigate WC for older adults by the types of staple foods, daily consumption of staple foods and types of cooking oil. Second, ordered logistic regression models were used for BMI. The two measures of panel data provided a heightened capacity to examine the complexity and dynamics of health behaviours.11 Our statistical tests were two-tailed with the threshold for significance set at 0.05 (i.e. p<0.05). Standardized regression coefficients (β) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were reported for OLS regression models, with results rounded to two decimal places. Adjusted odds ratios (AORs) and 95% CIs were reported for ordered logistic regression models. All models included the same set of primary predictors, controlling for the aforementioned covariates in all analyses. We conducted all data analyses with R statistical software (version 3.4.4; R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) using the package ‘plm’.13 All models included the aforementioned primary predictors and covariates.
Results
For male participants, the majority had normal BMI (67.1%) and the mean WC was 83.3±12.7 cm. For female participants, approximately 58.3% had normal BMI and the mean WC was 80.9±13.8 cm. The majority of participants consumed rice as the major staple food. More than 85% of older adults used vegetable and gingili cooking oils. Approximately 60% of older adults consumed fresh vegetables daily, whereas just 15% reported daily consumption of fruits. Most older adults consumed meat at least once a week. Most participants had lower levels of household income and education. Most female participants were not married, compared with 62% of older males who were married. Approximately 45.5% of male participants exercised and >60% reported good life satisfaction (refer to Table 1 for descriptive statistics).
Table 1.
Characteristics of the final study sample, CLHLS, 2011–2014 (N=6506)a
| Male | Female | |
|---|---|---|
| Variables | (n=3102) | (n=3404) |
| Obesity-related measurements | ||
| BMI, n (%) | ||
| Underweight | 514 (16.6) | 722 (21.2) |
| Normal | 2082 (67.1) | 1985 (58.3) |
| Overweight | 506 (16.3) | 697 (20.5) |
| Waist circumference (cm) | ||
| Mean±SD | 83.3±12.7 | 80.9±13.8 |
| Primary predictors and basic food consumption: | ||
| Types of staple food, n (%) | ||
| Rice | 1941 (62.6) | 2155 (63.3) |
| Corn | 110 (3.5) | 154 (4.5) |
| Wheat | 579 (18.7) | 612 (18.0) |
| Half rice, half wheat | 463 (14.9) | 467 (13.7) |
| Other | 9 (0.3) | 16 (0.5) |
| Amount of staple food consumed daily (liang), n (%) | ||
| 1–5 | 1387 (44.7) | 2109 (62.0) |
| 6–10 | 1562 (50.4) | 1241 (36.5) |
| >11 | 153 (4.9) | 54 (1.6) |
| Types of cooking oil, n (%) | ||
| Vegetable/gingili | 2714 (87.5) | 2934 (86.2) |
| Lard/other animal fat | 388 (12.5) | 470 (13.8) |
| Fresh vegetables consumption, n (%) | ||
| Daily | 1994 (64.3) | 2110 (62.0) |
| Quite often | 838 (27.0) | 963 (28.3) |
| Occasionally | 194 (6.3) | 229 (6.7) |
| Rarely or none | 76 (2.5) | 102 (3.0) |
| Fresh fruits consumption, n (%) | ||
| Daily | 453 (14.6) | 505 (14.8) |
| Quite often | 719 (23.2) | 793 (23.3) |
| Occasionally | 1064 (34.3) | 1175 (34.5) |
| Rarely or none | 866 (27.9) | 931 (27.4) |
| Meat consumption, n (%) | ||
| Daily | 1171 (37.7) | 1113 (32.7) |
| Weekly | 1307 (42.1) | 1365 (40.1) |
| Monthly | 285 (9.2) | 353 (10.4) |
| Occasionally | 166 (5.4) | 220 (6.5) |
| Rarely or none | 173 (5.6) | 353 (10.4) |
| Covariates | ||
| Age (years), n (%) | ||
| 60–80 | 1526 (49.2) | 1507 (44.3) |
| 81–95 | 1345 (43.4) | 1427 (41.9) |
| >95 | 231 (7.4) | 470 (13.8) |
| Marital status, n (%) | ||
| Married | 1929 (62.2) | 1031 (30.3) |
| Not married | 1173 (37.8) | 2373 (69.7) |
| Household income, n (%) | ||
| 1 | 1110 (35.8) | 1162 (34.1) |
| 2 | 799 (25.8) | 923 (27.1) |
| 3 | 457 (14.7) | 497 (14.6) |
| 4 | 206 (6.6) | 209 (6.1) |
| 5 | 343 (11.1) | 327 (9.6) |
| Do not know | 187 (6.0) | 286 (8.4) |
Table 1.
Continued
| Male | Female | |
|---|---|---|
| Variables | (n=3102) | (n=3404) |
| Years of formal education, n (%) | ||
| None | 875 (28.2) | 2455 (72.1) |
| 1–5 | 1191 (38.4) | 585 (17.2) |
| 6–10 | 839 (27.0) | 309 (9.1) |
| ≥11 | 197 (6.4) | 55 (1.6) |
| Current exercise status, n (%) | ||
| No | 1692 (54.5) | 2128 (62.5) |
| Yes | 1410 (45.5) | 1276 (37.5) |
| Number of times suffering from chronic diseases, n (%) | ||
| None | 2325 (75.0) | 2544 (74.7) |
| 1–2 | 647 (20.9) | 739 (21.7) |
| >2 | 130 (4.2) | 121 (3.6) |
| Self-rated life satisfaction, n (%) | ||
| Good | 1949 (62.8) | 2110 (62.0) |
| Neutral | 967 (31.2) | 1021 (30.0) |
| Bad | 143 (4.6) | 160 (4.7) |
| Not able to answer | 43 (1.4) | 113 (3.3) |
| Provinceb, n (%) | ||
| North | 136 (4.4) | 162 (4.8) |
| Northeast | 250 (8.1) | 204 (6.0) |
| East | 1298 (41.8) | 1334 (39.2) |
| Centre/South | 874 (28.2) | 1122 (33.0) |
| West | 544 (17.5) | 582 (17.1) |
| Type of community, n (%) | ||
| Urban | 1784 (57.5) | 1897 (55.7) |
| Rural | 1318 (42.5) | 1507 (44.3) |
SD: standard deviation.
Observations were provided by a total of 3253 survey participants in two waves (2011–2012 and 2014).
North: Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanxi; Northeast: Liaoning, Jilin, Heilongjiang; East: Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Fujian, Jiangxi, Shandong; Centre/South: Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Guangdong, Guangxi; West: Chongqing, Sichuan, Shaanxi.
Tables 2 and 3 are the results of OLS regression models and ordered logistic regression models, adjusted for all covariates with WC and BMI as outcomes, respectively. For staple foods, wheat consumption among male participants was significantly associated with greater WC than was rice consumption (β=2.84 [95% CI 1.55 to 4.13], p<0.01). This association was not observed among female participants (p>0.05). Half rice and half wheat consumption among males was also associated with greater WC than was rice consumption (β=2.24 [95% CI 0.93 to 3.56], p<0.01; Table 2). Older adults, both male and female, who consumed 6–10 liang of the staple food daily had greater WCs than those who consumed 1–5 liang daily. Participants who used animal-based cooking oils had smaller WCs than those who consumed vegetable-based cooking oils (p<0.05). The associations of cooking oils were similar in both male and female older adults (Table 2).
Table 2.
Estimates of WC from OLS regression models, controlling for all primary predictors and covariates, CLHLS, 2011–2014 (N=6506)
| Male | Female | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | β | 95% CI | β | 95% CI |
| Primary predictors and basic food consumption | ||||
| Types of staple food | ||||
| Rice | ||||
| Corn | −0.99 | −3.44 to 1.47 | −0.99 | −3.21 to 1.22 |
| Wheat | 2.84** | 1.55 to 4.13 | 0.83 | −0.51 to 2.18 |
| Half rice, half wheat | 2.24** | 0.93 to 3.56 | 1.29 | −0.11 to 2.69 |
| Other | 2.96 | −5.19 to 11.10 | −1.67 | −8.18 to 4.84 |
| Amount of staple food consumed daily (liang) | ||||
| 1–5 | ||||
| 6–10 | 1.17* | 0.25 to 2.10 | 1.16* | 0.22 to 2.11 |
| ≥11 | 1.23 | −0.88 to 3.35 | 2.73 | −0.85 to 6.31 |
| Types of cooking oil | ||||
| Vegetable/gingili | ||||
| Lard/other animal fat | −1.45* | −2.87 to −0.02 | −4.28** | −5.68 to −2.87 |
| Fresh vegetables consumption | ||||
| Daily | ||||
| Quite often | −0.17 | −1.23 to 0.89) | −1.38* | −2.46 to −0.31 |
| Occasionally | 0.67 | −1.21 to 2.55) | −1.90* | −3.75 to −0.04 |
| Rarely or none | −0.77 | −3.68 to 2.15) | −4.30** | −7.01 to −1.58 |
| Fresh fruits consumption | ||||
| Daily | ||||
| Quite often | −1.02 | −2.56 to 0.52 | −1.71* | −3.27 to −0.15 |
| Occasionally | −2.27** | −3.74 to −0.80 | −1.81* | −3.30 to −0.31 |
| Rarely or none | −1.79* | −3.31 to −0.26 | −1.09 | −2.66 to 0.48 |
| Meat consumption | ||||
| Daily | ||||
| Weekly | −0.55 | −1.56 to 0.45 | 0.50 | −0.59 to 1.58 |
| Monthly | −0.13 | −1.80 to 1.53 | 2.32** | 0.65 to 3.99 |
| Occasionally | −0.74 | −2.79 to 1.31 | 1.41 | 0.57 to 3.38 |
| Rarely or none | 0.19 | −1.85 to 2.23 | 2.33** | 0.67 to 4.00 |
| Covariates | ||||
| Age (years) | ||||
| 60–80 | ||||
| 81–95 | −0.77 | −1.76 to 0.22 | −1.97** | −3.05 to −0.89 |
| >95 | −2.80** | −4.66 to −0.93 | −5.18** | −6.75 to −3.61 |
| Marital status | ||||
| Married | ||||
| Not married | −0.19 | −1.17 to 0.78 | −1.10* | −2.16 to −0.03 |
| Household income | ||||
| 1 | ||||
| 2 | 0.88 | −0.28 to 2.04 | −0.87 | −2.03 to 0.30 |
| 3 | 2.63** | 1.21 to 4.04 | 0.48 | −0.96 to 1.92 |
| 4 | 1.09 | −0.83 to 3.01 | −0.84 | −2.84 to 1.15 |
| 5 | 1.92* | 0.32 to 3.52 | −0.48 | −2.18 to 1.23 |
| Do not know | 0.16 | −1.81 to 2.12 | 0.33 | −1.41 to 2.07 |
| Years of formal education | ||||
| None | ||||
| 1–5 | 0.95 | −0.15 to 2.05 | 1.03 | 0.21 to 2.27 |
| 6–10 | 1.48* | 0.24 to 2.73 | 0.75 | −0.92 to 2.43 |
| ≥11 | 0.29 | −1.76 to 2.34 | 2.38 | −1.22 to 5.97 |
(Continued)
Table 3.
Estimates of BMI from ordered logistic regression models, controlling for all primary predictors and covariates, CLHLS, 2011–2014 (N=6506)
| Male | Female | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | AOR | 95% CI | AOR | 95% CI |
| Primary predictors and basic food consumption | ||||
| Types of staple food | ||||
| Rice | ||||
| Corn | 1.12 | 0.74 to 1.71 | 0.80 | 0.56 to 1.15 |
| Wheat | 1.74** | 1.40 to 2.17 | 1.20 | 0.97 to 1.49 |
| Half rice, half wheat | 1.20 | 0.96 to 1.51 | 1.20 | 0.96 to 1.50 |
| Other | 1.72 | 0.44 to 6.63 | 0.98 | 0.35 to 2.73 |
| Amount of staple food consumed daily (liang) | ||||
| 1–5 | ||||
| 6–10 | 1.26** | 1.07 to 1.48 | 1.43** | 1.22 to 1.66 |
| ≥11 | 1.88** | 1.31 to 2.71 | 1.96* | 1.10 to 3.49 |
| Types of cooking oil | ||||
| Vegetable/gingili | ||||
| Lard/other animal fat | 0.81 | 0.63 to 1.03 | 0.65** | 0.52 to 0.81 |
| Fresh vegetables consumption | ||||
| Daily | ||||
| Quite often | 0.81* | 0.68 to 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.84 to 1.19 |
| Occasionally | 0.80 | 0.57 to 1.10 | 0.83 | 0.61 to 1.12 |
| Rarely or none | 0.56* | 0.34 to 0.94 | 0.54** | 0.35 to 0.84 |
| Fresh fruits consumption | ||||
| Daily | ||||
| Quite often | 0.96 | 0.74 to 1.25 | 0.62** | 0.48 to 0.79 |
| Occasionally | 0.74* | 0.57 to 0.95 | 0.68** | 0.53 to 0.86 |
| Rarely or none | 0.89 | 0.68 to 1.16 | 0.64** | 0.49 to 0.82 |
| Meat consumption | ||||
| Daily | ||||
| Weekly | 0.90 | 0.76 to 1.07 | 1.11 | 0.93 to 1.32 |
| Monthly | 0.81 | 0.61 to 1.08 | 1.06 | 0.81 to 1.38 |
| Occasionally | 0.94 | 0.67 to 1.34 | 1.11 | 0.81 to 1.52 |
| Rarely or none | 0.87 | 0.61 to 1.24 | 1.24 | 0.95 to 1.62 |
| Covariates | ||||
| Age (years) | ||||
| 60–80 | ||||
| 81–95 | 0.63** | 0.53 to 0.75 | 0.54** | 0.45 to 0.64 |
| >95 | 0.48** | 0.35 to 0.65 | 0.37** | 0.29 to 0.48 |
| Marital status | ||||
| Married | ||||
| Not married | 0.93 | 0.78 to 1.1 | 0.85 | 0.72 to 1.01 |
| Household income | ||||
| 1 | ||||
| 2 | 1.32** | 1.08 to 1.61 | 0.94 | 0.78 to 1.14 |
| 3 | 1.42** | 1.11 to 1.82 | 1.07 | 0.85 to 1.35 |
| 4 | 1.46* | 1.05 to 2.03 | 0.85 | 0.62 to 1.17 |
| 5 | 1.57** | 1.19 to 2.06 | 1.03 | 0.79 to 1.36 |
| Do not know | 0.91 | 0.65 to 1.28 | 0.91 | 0.69 to 1.21 |
| Years of formal education | ||||
| None | ||||
| 1–5 | 1.08 | 0.9 to 1.31 | 1.00 | 0.82 to 1.22 |
| 6–10 | 1.22 | 0.98 to 1.51 | 1.33* | 1.01 to 1.73 |
| ≥11 | 0.79 | 0.55 to 1.12 | 1.42 | 0.81 to 2.51 |
(Continued)
Table 2.
Continued
| Male | Female | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | β | 95% CI | β | 95% CI |
| Current exercise status | ||||
| No | ||||
| Yes | 1.18* | 0.24 to 2.12 | 1.37** | 0.40 to 2.35 |
| Number of times suffering from chronic diseases | ||||
| None | ||||
| 1–2 | 1.71** | 0.63 to 2.79 | 1.14* | 0.06 to 2.23 |
| >2 | 1.06 | −1.13 to 3.26 | −0.78 | −3.19 to 1.63 |
| Self-rated life satisfaction | ||||
| Good | ||||
| Neutral | 1.31** | 0.31 to 2.31 | −0.53 | 1.55 to 0.50 |
| Bad | 1.00 | −1.18 to 3.18 | −1.28 | −3.46 to 0.89 |
| Not able to answer | −1.33 | −5.16 to 2.50 | −4.52** | 7.09 to −1.95 |
| Province | ||||
| North | ||||
| Northeast | −0.57 | −3.24 to 2.11 | −0.29 | −3.25 to 2.67 |
| East | −3.45** | −5.76 to −1.14 | −1.92 | −4.32 to 0.48 |
| Centre/South | −4.85** | −7.29 to −2.41 | −1.74 | −4.24 to 0.76 |
| West | −5.39** | −7.90 to −2.88 | −2.90* | −5.50 to −0.30 |
| Type of community | ||||
| Urban | ||||
| Rural | −1.54** | −2.48 to −0.60 | −2.01** | −2.96 to −1.06 |
p<0.05, **p<0.01.
Table 3.
Continued
| Male | Female | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | AOR | 95% CI | AOR | 95% CI |
| Current exercise status | ||||
| No | ||||
| Yes | 1.08 | 0.92 to 1.27 | 1.20* | 1.02 to 1.40 |
| Number of times suffering from chronic diseases | ||||
| None | ||||
| 1–2 | 0.95 | 0.78 to 1.14 | 1.18 | 0.99 to 1.40 |
| >2 | 0.92 | 0.62 to 1.36 | 0.94 | 0.63 to 1.40 |
| Self-rated life satisfaction | ||||
| Good | ||||
| Neutral | 0.89 | 0.75 to 1.06 | 0.87 | 0.74 to 1.02 |
| Bad | 0.89 | 0.61 to 1.3 | 0.80 | 0.56 to 1.14 |
| Not able to answer | 0.6 | 0.31 to 1.16 | 0.60* | 0.39 to 0.90 |
| Province | ||||
| North | ||||
| Northeast | 0.9 | 0.58 to 1.39 | 0.90 | 0.57 to 1.42 |
| East | 0.55** | 0.38 to 0.8 | 0.65* | 0.44 to 0.94 |
| Centre/South | 0.50** | 0.33 to 0.75 | 0.51** | 0.35 to 0.76 |
| West | 0.51** | 0.33 to 0.76 | 0.63* | 0.42 to 0.95 |
| Type of community | ||||
| Urban | ||||
| Rural | 0.79** | 0.67 to 0.93 | 0.71** | 0.61 to 0.83 |
p<0.05, **p<0.01.
Similar to the WC model, wheat consumption among males was associated with a higher BMI than rice consumption (AOR 1.74 [95% CI 1.40 to 2.17], p<0.01). Again, this was not significant among Chinese older females. Higher staple food consumption was also associated with higher BMIs in both sexes. The use of animal-based cooking oils among female participants was associated with a lower mean BMI than the consumption of vegetable-based cooking oils. However, the finding of animal-based cooking oils did not attain statistical significance among Chinese older males.
Discussion
This research used panel analysis of a nationally representative sample to investigate the associations of staple food and cooking oil consumption by older adults with obesity-related WC and BMI measurements in China. A greater staple food consumption was significantly associated with higher levels of obesity among older adults. Specifically, among older males, wheat consumption was associated with higher levels of both WC and BMI. Similar findings were not observed among older females.
While rice is the main staple food in southern China, wheat in the form of noodles is the main staple food in northern China.14 Because rice contains large amounts of carbohydrates, there is a general misbelief that rice consumption leads to a higher incidence of obesity.15 However, previous research was unable to find such an association.16 Unlike rice, studies have demonstrated that wheat consumption is associated with obesity prevalence in the American, African and Asian regions, which may be a consequence of refined wheat-based foods introduced through Western dietary patterns.17 Similarly, maternal dietary intake of refined grains during pregnancy was associated with a higher prevalence of obesity among children.18 In this study, wheat consumption was associated with higher BMI and greater WC than rice consumption among older males. This association was also observed among half rice and half wheat male consumers for types of staple food and WC.
Although there is no differentiation between whole and refined wheat, Harris Jackson et al.19 found that replacing refined grains with whole grains in a weight-loss diet generally did not alter abdominal adipose tissue. Interestingly, Lee et al.20 pointed out that older adults consuming wheat had higher odds than rice consumers of reporting good quality of sleep. Furthermore, wheat consumption was associated with a lower risk of diet-related chronic diseases.21
Four potential rationales can be provided to support our research findings as compared with the discussions of wheat products and disease reduction by Dalton et al.21 First, the majority of survey participants in the present research were >80 y of age for both sexes. Participants’ age could help explain research gaps, as older adults are more prone to chronic diseases.5 Second, <20% of older adults in this study primarily consumed wheat products but >60% consumed rice as their major staple food. The disparity in consumption between rice and wheat products should be taken into consideration. Third, as the CLHLS questionnaires did not differentiate between whole grain and regular wheat products, the associated findings in this research may warrant further investigation. Lastly, participants’ BMIs and WCs were mostly within the normal range, therefore obesity was not prevalent in our study sample. Future research studies on wheat consumption by older Chinese adults are still needed to tease out the long-term relationships with health behaviours.
The findings for cooking oils were interesting. Animal-based cooking oils contain larger amounts of saturated fat, while consumption of vegetable-based cooking oils helps reduce low-density lipoprotein.22 Consumption of saturated fat is known to increase the chances of cardiovascular diseases and other chronic diseases.23 Vegetable-based cooking oils are the most common type of cooking oil used in China,24 as was evident in this study and was reported by >80% of respondents (Table 1). Contrary to popular belief, this study revealed that the consumption of animal-based cooking oils was associated with a lower WC and BMI among participants than the use of vegetable-based cooking oils. In terms of obesity prevention, it appears that there is no benefit in using vegetable-based cooking oils over animal-based oils. However, this finding might be attributed to the fact that a majority of the older participants included in the study sample had normal WC and BMI.
Kabagambe et al.25 reported that palm oil, a common type of vegetable cooking oil in developing countries, increased the odds of myocardial infarction. Given the well-established association between obesity and heart disease,26,27 a possible causal pathway may entail the consumption of vegetable-based cooking oils, with obesity either as an intermediate step or an effect modifier leading to heart disease. In fact, it has been discussed previously that some plant foods actually include higher amounts of saturated fat than animal foods. For example, coconut oil contains more than twice the amount of saturated fat found in beef fat.28 Therefore, clinical trials and studies are needed to establish the causal pathway and the underlying disease mechanism in order to examine the different effects of vegetable-based and animal-based cooking oils.
The Chinese central government is aware of these critical public health challenges and has proposed health promotional strategies to create a healthier environment for all residents, including the Healthy China 2030 plan. However, with the rapid shifts in dietary patterns, increasing obesity incidence and a fast-aging population,6,29,30 China faces the imminent need to revamp health promotion and preventive strategies. Health practitioners in China should continue monitoring dietary patterns, especially among the elderly, and actively promote obesity prevention programs. In principle, dieticians could collaborate with caregivers (such as social workers) to provide appropriate dietary advice and plans for the elderly to lower the risks of obesity. Krondl et al.31 suggested a plan for registered dieticians to serve as consultants to provide nutrition services for older communities. A similar approach can be adopted in China. For another example, when nutritionists and dieticians design dietary consumption planning for older adults, they should be aware of the importance of having a balanced diet to help maintain healthy lifestyles and prevent obesity among older Chinese adults.
This research has several strengths. It leverages a nationally representative database to examine the association of staple foods and cooking oils consumption—two key components in Chinese cuisine—with WC and BMI obesity-related measurements among older Chinese. In addition, studying the most common ingredients in the Chinese diet using a relatively large sample size and inclusion of the oldest old (>80 y of age) renders the findings more generalizable in the face of an aging population in China. Obesity in this study is defined by two indicators, WC and BMI, which minimizes misclassification bias associated with BMI-based obesity status among older adults.12 In this study, some similar findings were observed with either outcome. Besides, panel analysis is a more robust statistical technique than cross-sectional approaches for handling intra-individual variability in dietary changes over time.
This research is not without limitations. First, the questionnaire listed only vegetable and gingili oils as options for vegetable-based cooking oils. It is possible that different types of vegetable oil may alter the associations observed. Second, the CLHLS questionnaire includes only older adults’ dietary consumption behaviours; information was not available to calculate older adults’ caloric intake, which might be a confounding factor. Third, there is no information to differentiate wheat products that are gluten-free from those that are not. We also did not have information to identify the difference between regular and whole grain wheat products. Further research should consider the impact of differences between gluten-free and gluten wheat products and between regular and whole grain products on obesity measurements. Fourth, in order to capture the amount of staple food consumption accurately, we included only participants who knew and fully responded the amount of consumption. Therefore these study results can be applied only to those who knew the amount of staple food consumption, given that a substantial number of participants skipped or did not answer this question. This could be related to the participants’ age, as they may not be able to recall correctly the amount consumed. The study results cannot be applied to participants who did not provide the consumption information. Finally, self-reported bias could be an issue for dietary measurements, although the CLHLS investigators conducted one-on-one interviews for data collection. However, this is a common limitation for most research using secondary datasets and should not be a primary concern for this research.
Our research found that older men in China who consumed wheat as their staple food had greater WCs and higher BMIs than those who consumed rice. Increased staple food intake also correlated with higher obesity measurements, regardless of the participants’ sex. In addition, older women who consumed animal-based cooking oils had significantly lower WCs and BMIs than their counterparts who used vegetable-based cooking oils. A similar pattern was observed among older men for WC. Based on the study's results, using vegetable-based cooking oils was not associated with a lower level of obesity as compared with using animal-based oils. More observational studies, and possibly clinical trials, are needed to verify this relationship. In addition, health advisors should consider these findings when implementing public health or nutritional programs in China. Further research with similar interests should continue to target the older Chinese population to make conclusive claims. As previously mentioned, dieticians or nutritionists can work with public health practitioners to provide dietary guidelines and help older adults with their diet and lower the risk of obesity. In this way, when the prevalence of obesity is lower, the incidence of chronic diseases also might be lower in China as a whole.
Acknowledgements
Data used for this research were provided by the CLHLS managed by the Center for Healthy Aging and Development Studies, Peking University. The CLHLS is supported by funds from the U.S. National Institutes on Aging, China Natural Science Foundation, China Social Science Foundation and United Nations Population Fund. We thank research participants and researchers for their efforts in collecting the CLHLS data.
Contributor Information
Yen-Han Lee, Indiana University, School of Public Health, Department of Applied Health Sciences, Bloomington, IN 47401, USA.
Yen-Chang Chang, National Tsing Hua University, Center for General Education, Hsinchu City, Taiwan 300.
Ting Fang Alvin Ang, Boston University School of Medicine, Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology, Boston, MA 02118, USA; Boston University School of Medicine, Slone Epidemiology Center, Boston, MA 02118, USA.
Timothy Chiang, Pennsylvania State University, College of Medicine, Hershey, PA 17033, USA.
Mack Shelley, Iowa State University, Department of Political Science and Department of Statistics, Ames, IA 50011, USA.
Ching-Ti Liu, Boston University, School of Public Health, Department of Biostatistics, Boston, MA 02118, USA.
Authors’ contributions
Y-HL and Y-CC conceived the study design and conducted the statistical analyses. Y-HL, TFAA and TC prepared the manuscript. MS, TFAA and C-TL critically revised the manuscript. TFAA and C-TL provided technical support.
Funding
None.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest for this present research.
Ethical approval
Not required.
Data availability
Chinese Longitudinal Healthy Longevity Survey (https://doi.org/10.3886/ICPSR36692.v1).
References
- 1. Lee Y, Chiang TC, Liu CTet al. . Investigating adolescents’ sweetened beverage consumption and Western fast food restaurant visits in China, 2006–2011. Int J Adolesc Med Health. 2018; doi: 10.1515/ijamh-2017-0209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Xu X, Hall J, Byles Jet al. . Dietary pattern is associated with obesity in older people in China: data from China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS). Nutrients. 2015;7(9):8170–88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Xu X, Byles J, Shi Zet al. . Dietary pattern transitions, and the associations with BMI, waist circumference, weight and hypertension in a 7-year follow-up among the older Chinese population: a longitudinal study. BMC Public Health. 2016;16:743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Hou JK, Li K. The ageing of the Chinese population and the cost of health care. Soc Sci J 2011;48(3):514–26. [Google Scholar]
- 5. Wang XQ, Chen PJ. Population ageing challenges health care in China. Lancet. 2014;383(9920):870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Smith JP, Strauss J, Zhao Y. Healthy aging in China. J Econ Ageing. 2014;4:37–43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Mezuk B, Chen Y, Yu Cet al. . Depression, anxiety, and prevalent diabetes in the Chinese population: findings from the China Kadoorie Biobank of 0.5 million people. J Psychosom Res. 2013;75(6):511–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Hu EA, Pan A, Malik Vet al. . White rice consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes: meta-analysis and systematic review. BMJ. 2012;344:e1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Ng CY, Leong XF, Masbah Net al. . Heated vegetable oils and cardiovascular disease risk factors. Vascul Pharmacol. 2014;61(1):1–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Hai S, Cao L, Yang Xet al. . Association between nutrition status and cognitive impairment among Chinese nonagenarians and centenarians. Int J Gerontol. 2017;11(4):215–9. [Google Scholar]
- 11. Hsiao C Panel data analysis—advantages and challenges. TEST. 2007;16:1–22. [Google Scholar]
- 12. Hu F Measurements of adiposity and body composition. In: Hu F, editor. Obesity epidemiology. New York: Oxford University Press; 2008, p. 53–83. [Google Scholar]
- 13. Croissant Y, Millo G. Panel data econometrics in R: the plm package. J Stat Softw. 2008;27(2);1–43. [Google Scholar]
- 14. Ma G Food, eating behavior, and culture in Chinese society. J Ethn Foods. 2015;2(4):195–9. [Google Scholar]
- 15. Brody JE The fats you don't need to fear, and the carbs that you do. New York Times, 19 October 2015 Available from: https://cn.nytimes.com/health/20160303/t03fats/zh-hant/dual/[accessed 7 July 2018]. [Google Scholar]
- 16. Kolahdouzan M, Khosravi-Boroujeni H, Nikkar Bet al. . The association between dietary intake of white rice and central obesity in obese adults. ARYA Atheroscler. 2013;9(2):140–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. You W, Henneberg M. Cereal crops are not created equal: wheat consumption associated with obesity prevalence globally and regionally. AIMS Public Health. 2016;3(2):313–28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Zhu Y, Olsen SF, Mendola Pet al. . Maternal dietary intakes of refined grains during pregnancy and growth through the first 7 y of life among children born to women with gestational diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr. 2017;106(1):96–104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Harris Jackson K, West SG, Vanden Heuvel JPet al. . Effects of whole and refined grains in a weight-loss diet on markers of metabolic syndrome in individuals with increased waist circumference: a randomized controlled-feeding trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;100(2):577–86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Lee Y, Chang Y, Lee Yet al. . Dietary patterns with fresh fruits and vegetables consumption and quality of sleep among older adults in mainland China. Sleep Biol Rhythms. 2018;16:293–305. [Google Scholar]
- 21. Dalton SM, Tapsell LC, Probst Y. Potential health benefits of whole grain wheat components. Nutr Today. 2012;47(4):163–74. [Google Scholar]
- 22. Wang Y, Liu C. Pick the right oil, use the good oil. Bureau of National Health Insurance, Department of Health, Executive Yuan, 2011. Available from:https://www.nhi.gov.tw/epaper/ItemDetail.aspx?DataID=2410&IsWebData=0&ItemTypeID=5&PapersID=203 [accessed 10 July 2018] [in Mandarin Chinese]. [Google Scholar]
- 23. Briggs MA, Petersen KS, Kris-Etherton PM. Saturated fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: Replacements for saturated fat to reduce cardiovascular risk. Healthcare (Basel). 2017;5(2):29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Ma G, Hao L, Li Yet al. . Cooking oil consumption of adults in China [in Mandarin Chinese] Food Nutr China. 2008;9:29–32. [Google Scholar]
- 25. Kabagambe EK, Baylin A, Ascherio Aet al. . The type of oil used for cooking is associated with the risk of nonfatal acute myocardial infarction in Costa Rica. J Nutr. 2005;135(11):2674–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Eckel RH Obesity and heart disease: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Nutrition Committee, American Heart Association. Circulation. 1997;96(9):3248–50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Kenchaiah S, Evans J, Levy Det al. . Obesity and the risk of heart failure. N Engl Med. 2002;347(5):1887–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Ede G The brain needs animal fat-why humans can't thrive on plants alone. Available from:https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/diagnosis-diet/201903/the-brain-needs-animal-fat[accessed 13 June 2020].
- 29. Wu Y Overweight and obesity in China: the once lean giant has a weight problem that is increasing rapidly. BMJ . 2006;333:362–3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Zhai F, Du S, Wang Zet al. . Dynamics of the Chinese diet and the role of urbanicity, 1991–-2011. Obes Rev. 2014;15(Suppl 1):16–26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Krondl M, Coleman P, Lau D. Helping older adults meet nutritional challenges. J Nutr Elder. 2008;27(3–4):205–20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Chinese Longitudinal Healthy Longevity Survey (https://doi.org/10.3886/ICPSR36692.v1).


