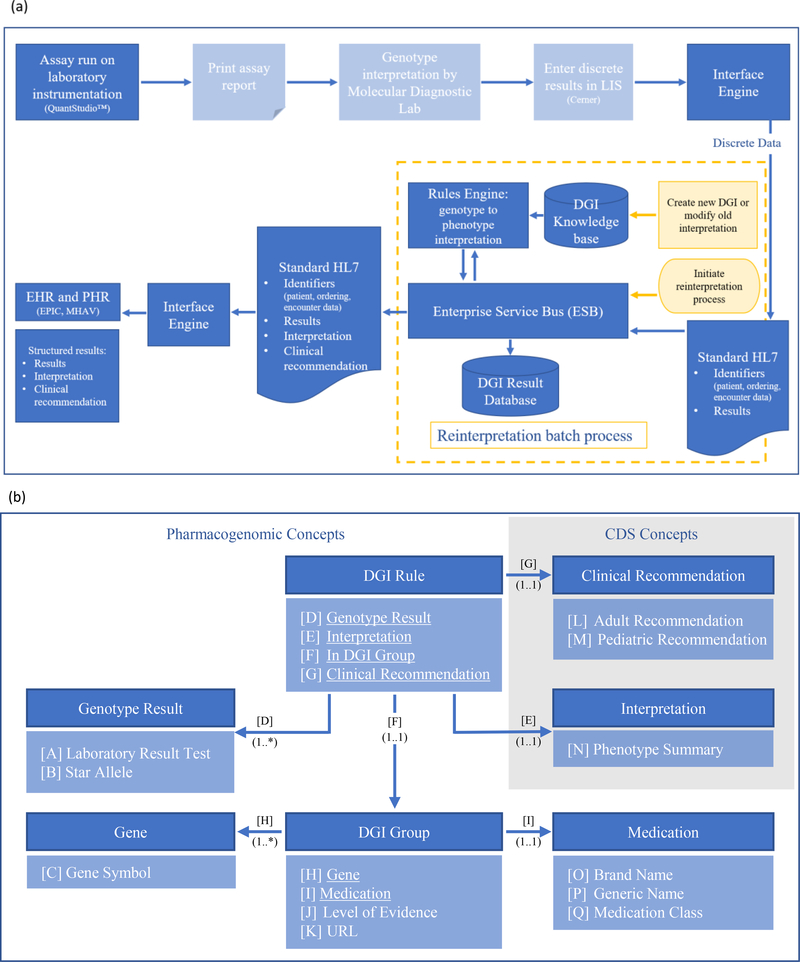
Figure 4.
Knowledge management for pharmacogenomics data.
(a) An overview of the PREDICT informatics infrastructure. Genotype resulting and phenotype interpretation of new patients is shown in the blue boxes, with light shading indicating manual steps and dark shading indicating automated steps. Yellow boxes indicate steps for phenotype reinterpretation for patients with existing results. The DGI knowledge base stores knowledge content required for interpretation and clinical recommendations. The DGI result database stores longitudinal patient specific results and interpretation which allows for real-time data reprocessing. LIS – laboratory information system; DGI – drug-gene interaction; HL7 – Health Level Seven standards; EHR – electronic health record; PHR – patient health record; MHAV – My Health at Vanderbilt.
(b) Domain Model of the PREDICT knowledge base high-level concepts represented as a unified modeling language class diagram. This class diagram illustrates the concepts and relationships of the PREDICT domain. Concepts of the domain are depicted by dark blue shading with attributes and relationships (underlined) listed below the name of each concept in light blue shading. Associations across the elements are represented by labeled arrows. DGI Group concept represents the drug-gene associations, while DGI Rule links this concept to genotype results, interpretations and associated clinical recommendations. Once stored in a particular patient’s EHR, interpretations fire the CDS upon ordering the medication represented within the DGI Group concept, while associated patient and provider facing clinical recommendations provide the appropriate guidance. DGI – drug-gene interaction; CDS – clinical decision support; URL – uniform resource locator.