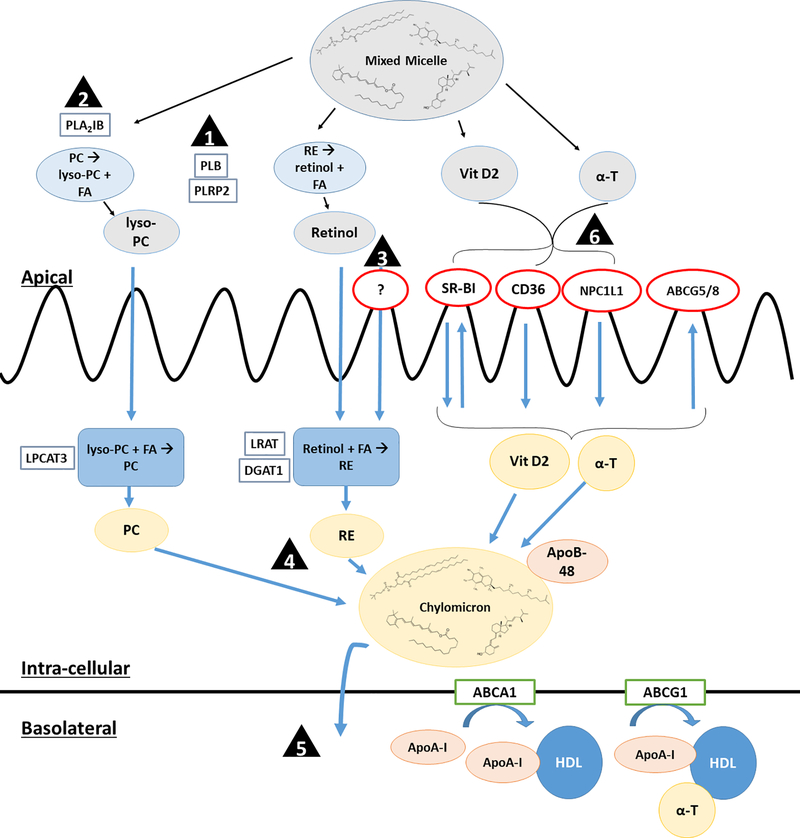
Figure 2.
Schematic of potential points of differences in FSV absorption between MetS and control subjects: (1) Increased PLB and PLRP2 expression and/or activity in MetS may increase retinyl ester hydrolysis and uptake. (2) Increased PLA2IB activity, leading to increased luminal lyso-PC, may increase chylomicron secretion and contribute to increased retinyl ester absorption in MetS subjects. (3) Unidentified retinol-specific apical transport protein may lead to increased retinol uptake in MetS. (4) Vitamin A absorption may be linked to the increased lipemic response observed in MetS, either due to increased chylomicron production and/or decreased clearance. (5) Increased SM in chylomicrons of MetS persons may delay chylomicron clearance, contributing to elevated vitamin A measured in this fraction. (6) Vitamins D and E compete for transporters in in vitro models; however, clinical studies are warranted to investigate the effects of this antagonism in vivo. Abbreviations: ABCA1 = ATP-binding cassette transporter sub-family A member 1, ABCG1 = ATP-binding cassette transporter sub-family G member 1, ABCG5/8 = ATP-binding cassette transporter sub-family G members 5/8, ApoB-48 = apolipoproteinB-48, ApoA-I = Apolipoprotein A-I, α-T = α-tocopherol, CD36 = cluster of differentiation 36, DGAT1 = diglyceride acyltransferase 1, HDL = high density lipoprotein, LPCAT3 = lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3, LRAT = lecithin retinol acyltransferase, lyso-PC = lysophosphatidylcholine, NPC1L1 = Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1, PC = phosphatidylcholine, PLA2IB = phospholipase A2 group IB, PLB = brush border phospholipase B, PLRP2 = pancreatic lipase-related protein 2, RE = retinyl ester, SM = sphingomyelin, SR-BI = scavenger receptor class B type 1, Vit D2 = ergocalciferol.