Figure 3.
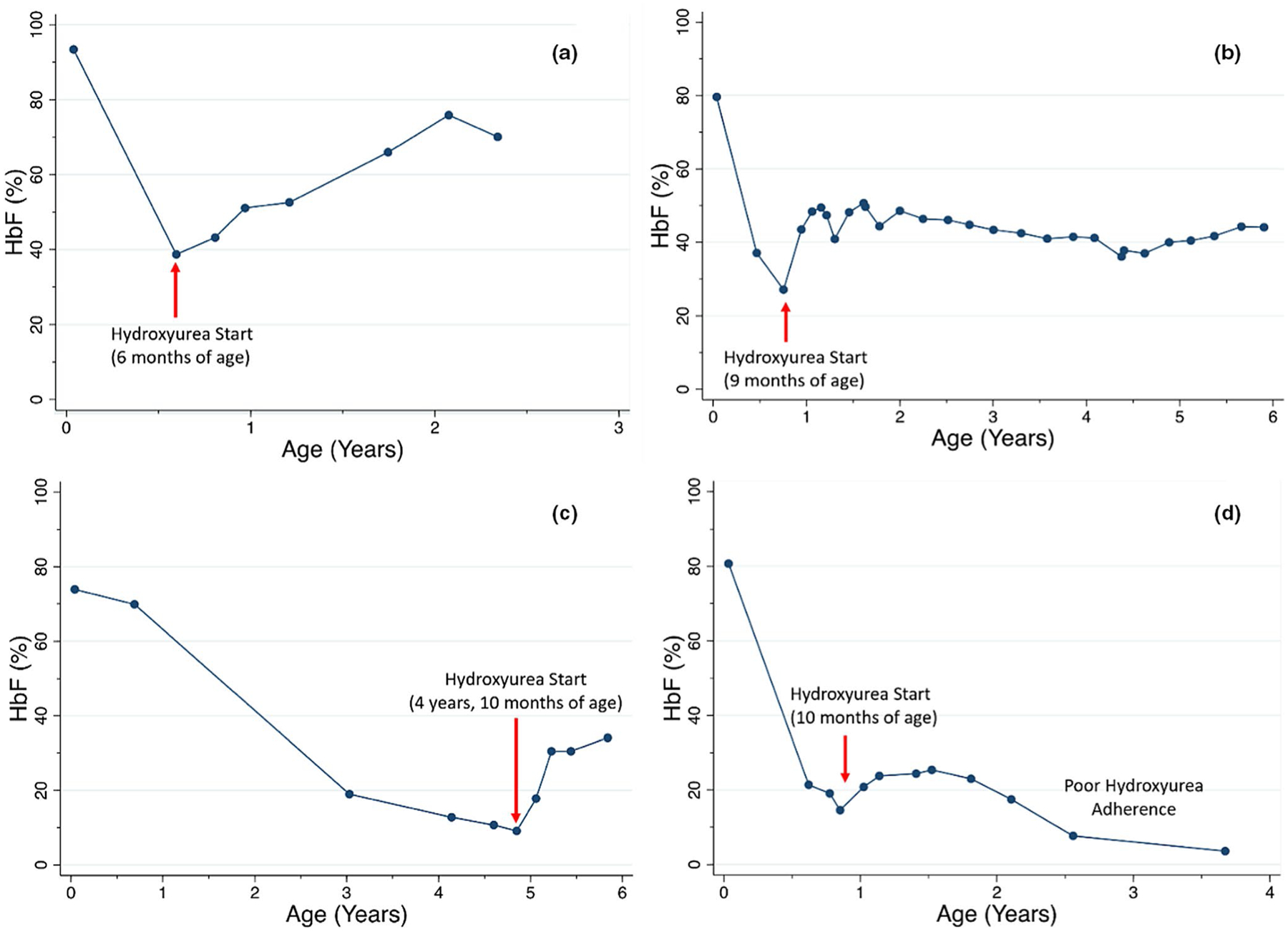
Fetal hemoglobin (HbF) induction with individualized hydroxyurea dosing. With individualized, pharmacokinetic-guided dosing, participants enrolled in the Therapeutic Response Evaluation and Adherence Trial (TREAT) study achieved and sustained HbF levels beyond 30–40% for children initiating hydroxyurea at young ages (a, b) and older ages, beyond the expected time of HbF silencing (c). For infants beginning hydroxyurea as early as 6 months of age, HbF levels increased to >70% a. Medication nonadherence is an important factor, as HbF levels sharply decline when hydroxyurea is not taken as prescribed (d).
