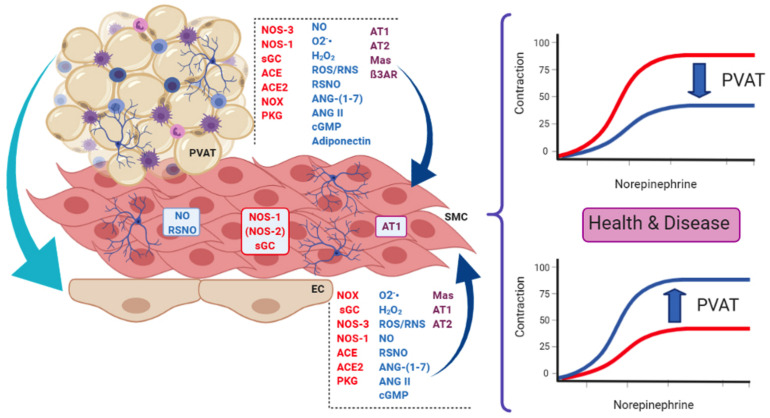
FIGURE 1.
Some of the main actors present in endothelial cells (EC) and perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT) that influence smooth muscle cells (SMC) in the context of the present review. PVAT can also modulate endothelial function and influence the vascular tone. These actors are involved in the dual role of PVAT, namely, its anti-contractile (upper curves) and pro-contractile (lower curves) effects on vessel response, both relevant in health and disease. Enzymes are in red letters, mediators in blue, and receptors/effectors in purple. PVAT contains adipocytes, innervation (neurons) and immune cells (lymphocytes, macrophages, and eosinophils), and vessels (not shown). NOS-3, NOS endothelial isoform; NOS-1, NOS neuronal isoform; (NOS-2), NOS inducible isoform; NOX, NADPH oxidases; sGC, soluble guanylate cyclase; ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme; ACE2, ACE isoform 2; NO, nitric oxide; O2-, superoxide anion; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; ROS/RNS, reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, respectively; RSNO, low-molecular weight and protein S-nitrosothiols; ANG-(1–7), angiotensin 1–7; ANG II, angiotensin II; cGMP, cyclic GMP; AT1, angiotensin AT1 receptor; AT2, angiotensin AT2 receptor; Mas, Mas receptor; ß3AR, beta-3 adrenergic receptor; PKG, protein kinase G.