FIGURE 2.
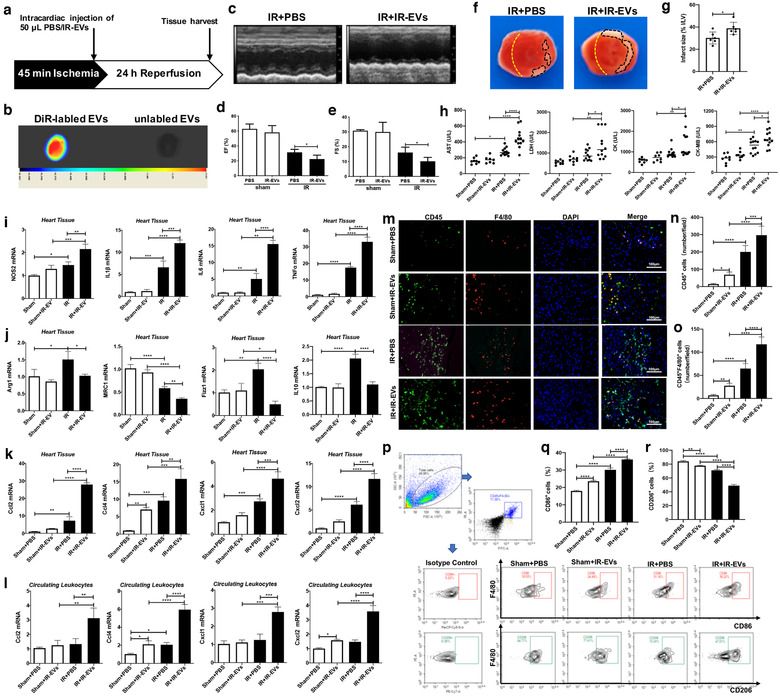
IR‐EVs transfusion aggravate IR injury and facilitate M1 polarization of macrophage in the heart. [(a) Protocol schematic for infusion of IR‐EVs and tissue harvest. (b) Bioluminescence imaging confirmed that IR‐EVs were retained within the heart by intracardiac injection of DiR‐labelled IR‐EVs. (c) Representative echocardiogram. Statistical results of (d) EF value, and (e) FS value (n = 6). (f) Representative TTC‐stained hearts from mice sacrificed 1 day after IR‐EVs or PBS transfusion. (g) Statistical results of the infarct size (represented with infarct area (I) / left ventricular (LV) area) in (f) (n = 6). (h) Plasma levels of myocardial enzymes, including AST, LDH, CK and CK‐MB (n = 8, 8, 12, 12). (i) The expression of NOS2, IL1β, IL6 and TNFα in the heart. (j) The expression of M2‐polarization related genes including Arg1, MRC1, Fizz1 and IL10 in the heart. The expression of chemokines including Ccl2, Ccl4, Cxcl1 and Cxcl2 in (k) the heart and (l) the circulating leukocytes. (m) Representative immunofluorescence images showed the CD45+ inflammatory cells and CD45+F4/80+ macrophages in the heart. (n) Statistical results of CD45+ inflammatory cells (cell counts per field) in the cardiac immunofluorescence images. (o) Statistical results of CD45+F4/80+ macrophages (cell counts per field) in the cardiac immunofluorescence images. (p) Polarization of macrophages in the heart determined by flow cytometry. (q) Percentage of CD86+ M1 polarized macrophage in the heart. (r) Percentage of CD206+ M2 polarized macrophage in the heart. *, P < 0.05;**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P<0.0001]
