Fig. 1.
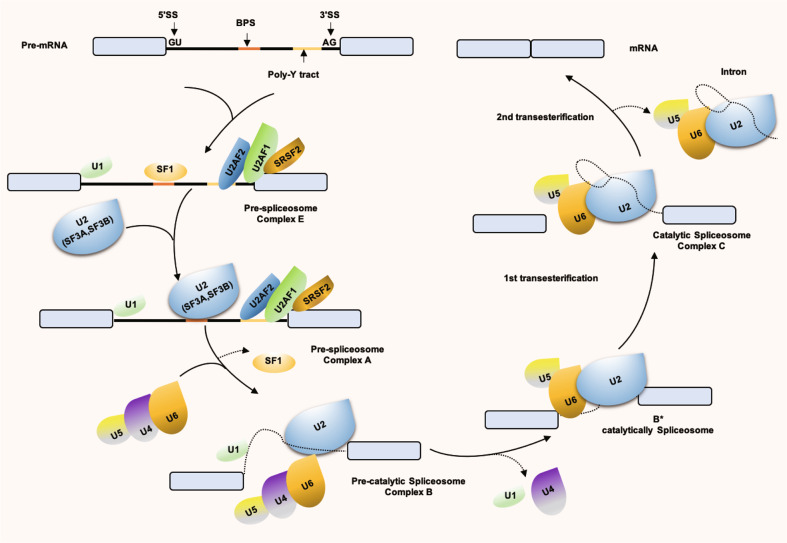
Spliceosome assembly. U1 snRNP recognizes 5′ SS and binds through base-pairing, SF1 binds to BPS, U2AF2 binds to polypyrimidine tract and U2AF1 binds to 3′ SS, forming Complex E. Next, U2 snRNP, with the assistance of U2AF, replaces SF1 with the BPS through base-pairing to form Complex A. Next, U5/U4/U6 is recruited and results in the rearrangement of Complex A. Among them, U4 and U6 snRNP are combined through complementary pairing of their RNA components, while U5 snRNP is loosely bound through protein interaction, at which time a Complex B is formed. Through a series of conformational changes, U1 snRNP leaves, U6 snRNP binds to 5′ SS, and at the same time, U4 snRNP leaves so that U6 snRNP and U2 snRNP pair through snRNA. After this rearrangement process, Pre-catalytic Spliceosome Complex B is formed, followed by two transesterification reactions. The first transesterification reaction generates Complex C. The rearrangements occur in Complex C, promoting second transesterification, resulting in a post-spliceosomal complex. As a result, exons are interconnected to form mature mRNA, introns are degraded and snRNPs are recycled. SF1 splicing factor 1, BPS branch point sequence, SS splice-site, snRNPs small nuclear RNPs