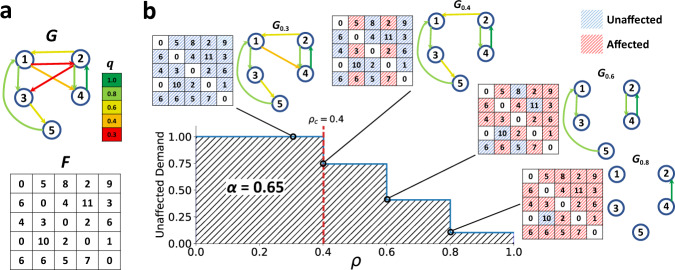
Fig. 1. Percolation on an example demand-serving network.
a Network G with size n = 5, where quality qij of each link eij is color-coded (according to the color-bar). Matrix F quantifies the flow demand between all pairs of nodes which sums up to 100 units in total. b The percolation process is simulated by increasing a threshold ρ while removing links eij with qij ≤ ρ. Subnetwork Gρ is visualized at different ρ’s with its corresponding affected (red) and unaffected (blue) flow demand color-coded in matrix F. In this example, by definition, the system collapses at ρc = 0.4, when the 5-nodes strongly connected GC disintegrates into two strongly connected components of sizes 2 and 3, while unaffected demand (UD) is still at 75%. The reliability of the network G is α = 0.65, found by calculating the area under the curve of UD versus ρ.