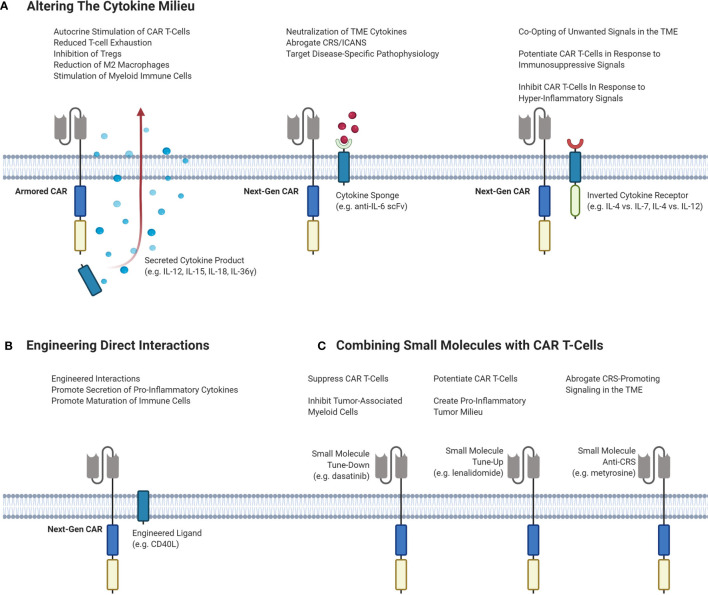
Figure 3.
Different strategies of targeting the TME to enhance the efficacy and decrease the toxicity of CAR T-cells. (A) Potential CAR T-cell strategies that can modulate the cytokine milieu in the TME. Armored CARs are second-generation CARs that are engineered to secrete a cytokine product of interest to stimulate inflammation and inhibit immunosuppressive cells and signals. Next-Gen CARs can be engineered to neutralize cytokines to dampen CRS/ICANS or to target pathophysiological signaling. Next-Gen CARs can also be engineered to co-express an inverted cytokine receptor that can co-opt various signals in the TME. This can be done to tune-up CAR T-cells in response to immunosuppressive signaling, or to tune-down CAR T-cells in response to hyper-inflammatory signaling to abrogate CRS. (B) Engineering CAR T-cells to express a ligand of interest on the T-cell surface to induce interactions or signaling pathways of interest. (C) Small molecules can be administered to achieve different effects with CAR T-cells. Small molecules can serve to either tune-up or tune-down CAR T-cells or be used to abrogate CRS-potentiating signaling. CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; Treg, regulatory T-cell; TME, tumor microenvironment; CRS, cytokine release syndrome; ICANS, immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome; IL, interleukin; scFv, single-chain variable fragment.