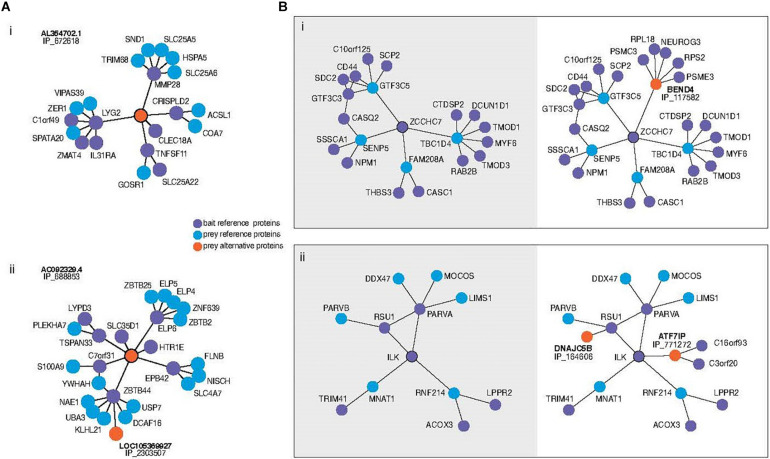
FIGURE 1.
(A) Subnetworks of alternative proteins identified in the most comprehensive human protein-protein interaction network (Leblanc et al., 2020). Direct neighbors and neighbors of neighbors (here called second neighborhood) are shown around alternative proteins encoded by genes of “non-coding” biotypes revealing previously unknown physical interaction network structure. Alternative protein IP_672618 relates regions otherwise not connected (i). The authors speculate that the bridging role of IP_688853 between ELP6 and other proteins could yield insight into the mechanism of tumorigenesis recently associated with this gene. Bait proteins are reference (annotated) proteins expressed with a tag for purification from which prey proteins are identified. “IP_” protein accessions refer to OpenProt 1.6 unique identifiers for alternative proteins. (B) Second neighborhoods of two reference proteins extracted from the same network with (right) and without (left) alternative proteins. Inclusion of an alternative protein from the dual coding gene BEND4 reveals the addition of a hub around the protein ZCCHC7 (i). Addition of two alternative proteins in the second neighborhood of ILK increases the betweenness centrality of the ILK-RSU1-PARVA clique (ii).