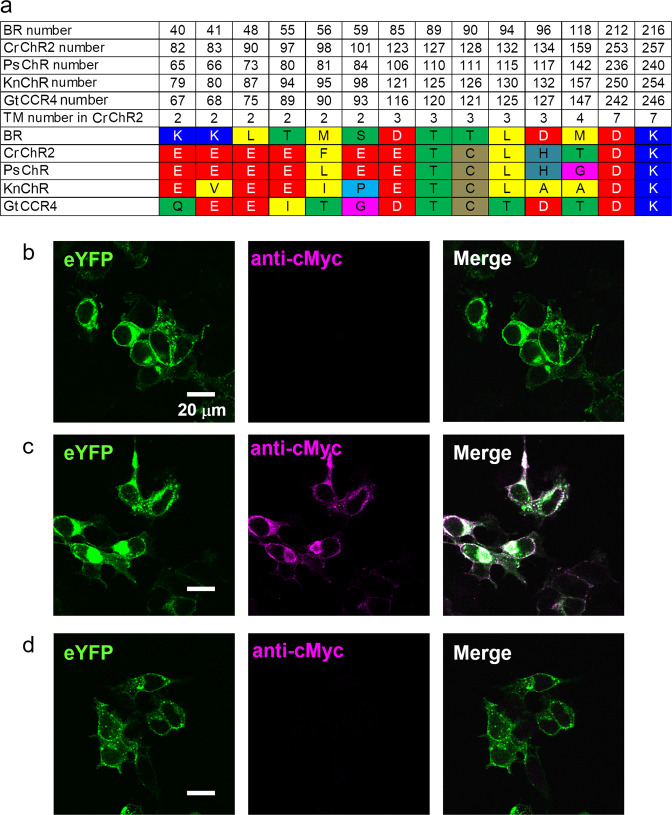
Fig. 1. Sequence comparison and determination of KnChR transmembrane topology and orientation.
a Amino acid alignments of bacteriorhodopsin (BR), CrChR2 (Channelrhodopsin-2 from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii), PsChR (Channelrhodopsin from Platymonas subcordiformis), KnChR and GtCCR4 (Cation Channelrhodopsin-4 from Guillardia theta). The characteristic amino acids in BR and CrChR2 were selected. In addition, amino acid numbers of each protein and transmembrane helix (TM) number are indicated. See Supplementary Fig. 1 for an alignment of the whole protein sequences. b Immunostaining of KnChR. Expression of KnChR-3.0-eYFP-cMyc in cultured ND7-23 cells, with KnChR bearing the c-Myc epitope tag at the C-terminus. eYFP fluorescence (left, green), probed with a c-Myc antibody under non-permeabilized conditions for immunofluorescent staining with Alexa Fluor 594 (middle, magenta) and merge (right). Scale bar, 20 μm. c Expression of KnChR-3.0-eYFP-cMyc in cultured ND7-23 cells. eYFP fluorescence (left, green), probed with a c-Myc antibody under permeabilized conditions (0.5% Triton X-100) for immunofluorescent staining with Alexa Fluor 594 (middle, magenta) and merge (right). d Expression of KnChR-3.0-eYFP in cultured ND7-23 cells. eYFP fluorescence (left, green), probed with a c-Myc antibody under permeabilized conditions (0.5% Triton X-100) for immunofluorescent staining with Alexa Fluor 594 (middle, magenta) and merge (right).