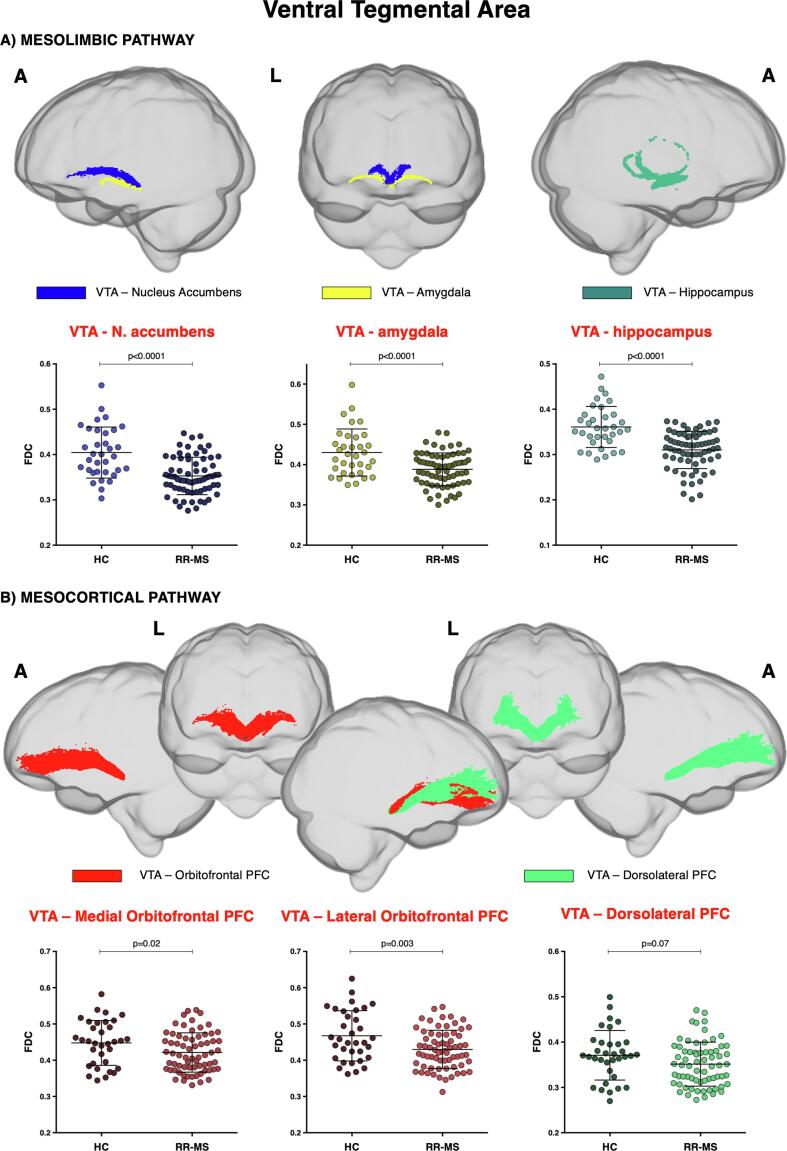
Fig. 3.
Mesocorticolimbic fibre tract-specific significant FDC decreases in patients with multiple sclerosis (RR-MS) compared to healthy control (HC). Tracts of interest projecting from ventral tegmental area (VTA) are shown in glass brain representations using the mrview tool in MRtrix3. A) mesolimbic pathway encompasses the tracts connecting VTA with nucleus accumbens, amygdala, and hippocampus; B) mesocortical pathway encompasses VTA projections to medial and lateral orbitofrontal and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (PFC). Differences in average FDC between HC and RR-MS patients in the selected white matter tracts of the A) mesolimbic and B) mesocortical pathway are shown in scatter plots. Comparisons were tested by independent sample t-tests. The statistical threshold was set to p < 0.003 after Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons (FDC = fibre-density cross-section, A = anterior, L = left).