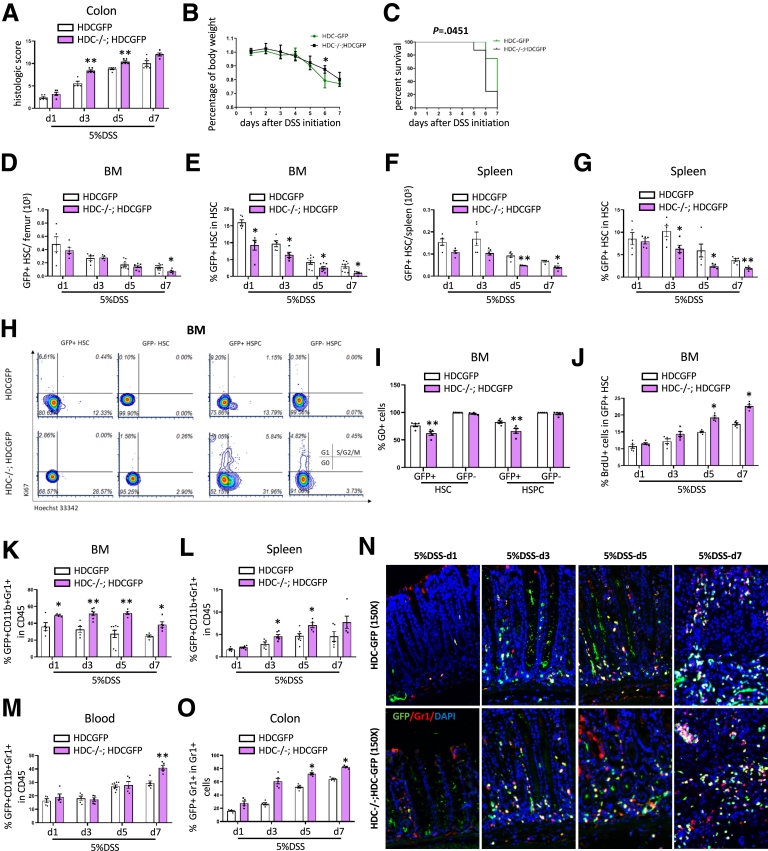
Figure 4.
HDC deficiency leads to greater depletion and activation of MB-HSCs in DSS-induced acute colitis and promotes greater recruitment of HDC+ myeloid cells in the colon. (A) Comparison of the severity of DSS-induced acute colitis in HDC-/-; HDC-GFP mice, and HDC-GFP mice were evaluated by histopathologic scoring of H&E-stained slides. (B) Analysis of body weight change and (C) Kaplan–Meier curve depicting survival rates of HDC-GFP mice and HDC-/-; HDC-GFP mice at different time points of 5% DSS treatment. Total number of (D) BM GFP+HSCs and the (E) percentage of GFP+ HSCs among total HSCs from HDC-/-; HDC-GFP mice compared with HDC-GFP mice at different time points of 5% DSS treatment. Total number of (F) splenic GFP+ HSCs and the (G) percentage of GFP+ HSCs among total HSCs from HDC-/-; HDC-GFP mice compared with HDC-GFP mice at different time points of 5% DSS treatment. (H) Cell-cycle analysis with FACS for Ki67 and Hoechst 33342 staining and the (I) percentage of G0 cells of BM HSCs and HSPCs from HDC-GFP mice and HDC-/-; HDC-GFP mice at 5 days after 5% DSS treatment. (J) Percentage of BrdU+ cells of BM GFP+ HSCs of HDC-/-; HDC-GFP mice compared with HDC-GFP mice at different time points of 5% DSS treatment. Percentage of GFP+ myeloid cells among CD45+ cells in (K) BM, (L) spleen, and (M) blood of HDC-GFP mice and HDC-/-; HDC-GFP mice at different time points of 5% DSS treatment. (N) Immunofluorescent images showing GFP+Gr1+ cells in the distal colon from HDC-GFP mice and HDC-/-; HDC-GFP mice at different time points of 5% DSS treatment. (O) Quantification of the percentage of GFP+ Gr1+ cells among all GFP+ cells. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. Results are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.