Figure 4.
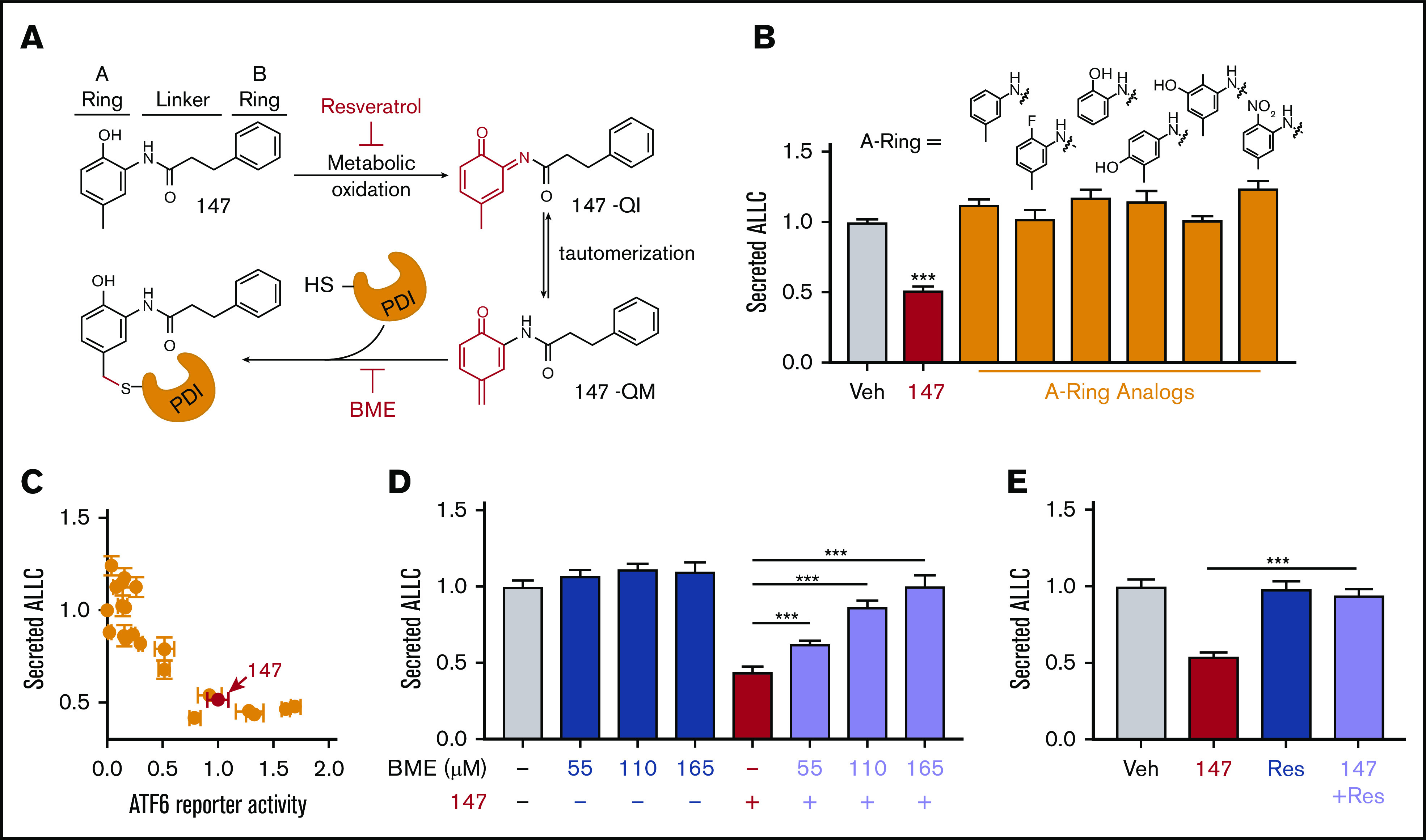
Compound 147 reduces ALLC secretion through a mechanism involving compound metabolic activation and covalent protein modification. (A) Illustration showing the metabolic activation of 147 to a quinone imide (147-QI) and quinone methide (147-QM). These reactive electrophiles covalently modify ER proteins, including multiple PDIs. The A ring, linker, and B ring of 147 are indicated. Specific steps inhibited by resveratrol (Res) and β- mercaptoethanol (BME) are also indicated. Adapted from Paxman et al.39 (B) Graph showing normalized amounts of ALLC in conditioned media from ALMC-2 cells treated for 18 hours with vehicle (Veh), 147 (10 µM), or the indicated 147 A ring analog (10 µM). ALLC was quantified by ELISA. Error bars show standard error of the mean (SEM) for 10 replicates across 2 independent experiments. (C) Plot comparing the normalized activation of an ATF6-selective luciferase reporter in HEK293 cells39 with reductions in ALLC secretion from ALMC-2 cells for 147 (10 µM) or 147 analogs containing alterations to the A ring, linker, and B ring. Error bars for the ATF6 reporter activation show SEM for 3 independent experiments. Error bars for ALLC secretion show 10 replicates across 2 independent experiments. (D) Graph showing normalized amounts of ALLC secretion from ALMC-2 cells treated for 18 hours with Veh or 147 (10 µM) and/or BME, as indicated. ALLC was quantified by ELISA. Error bars show SEM for 10 replicates across 2 independent experiments. (E) Graph showing normalized ALLC secretion from ALMC-2 cells treated for 18 hours with Veh, 147 (10 µM), and/or Res (10 µM), as indicated. ALLC was quantified by ELISA. Error bars show SEM for 9 replicates across 2 independent experiments. ***P < .005 vs Veh (unpaired Student t test; B);*** P < .005 (paired Student t test; D-E).
