Figure 3. CYP39A1 Association With Presence of Exfoliation Syndrome.
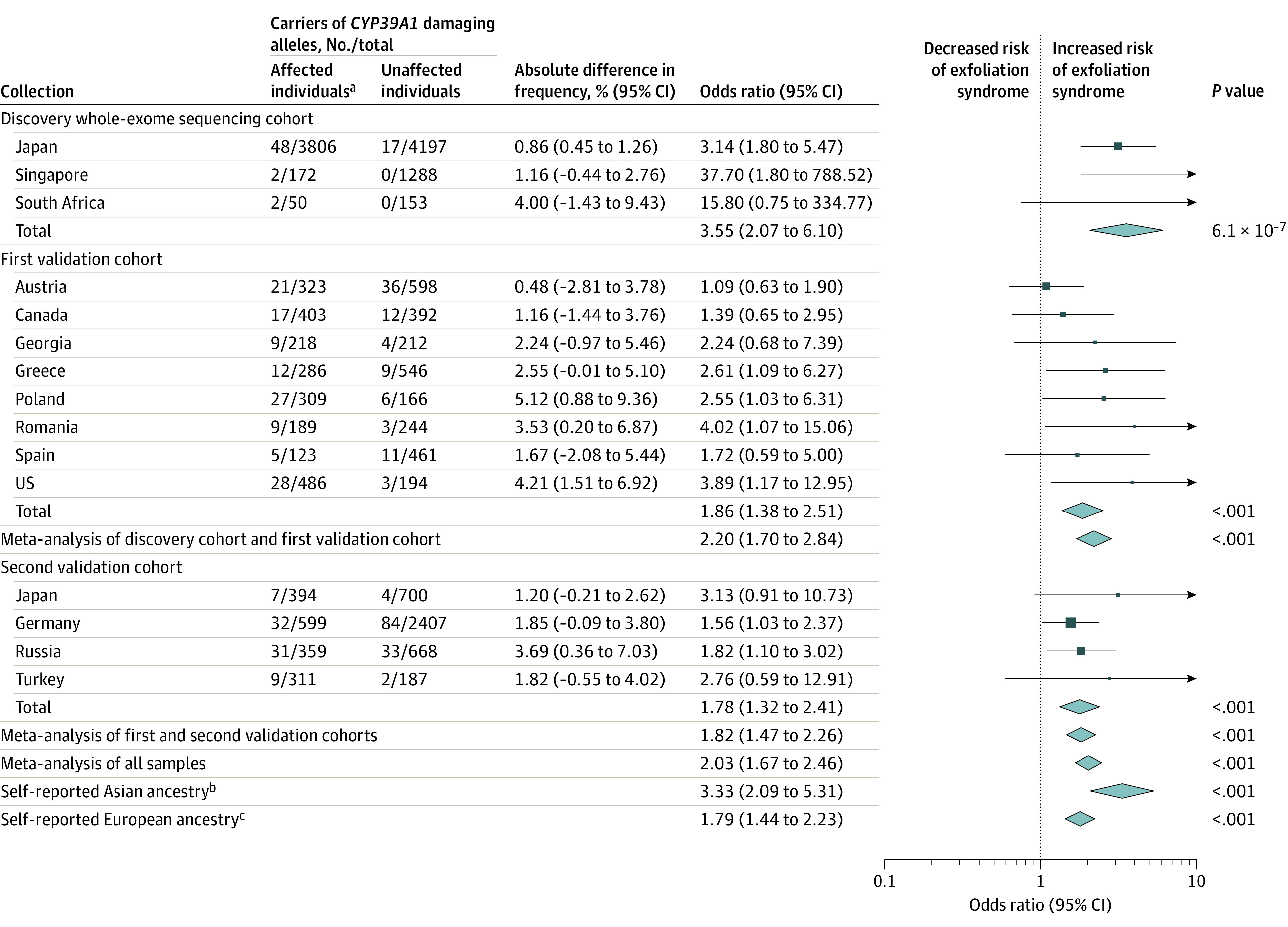
Forest plot describing the association between the burden of damaging CYP39A1 allelic variants and exfoliation syndrome among 20 441 participants from 14 countries. The height of the data marker is proportional to the size of the sample. The width of the diamond represents the 95% CI. P values were calculated using the Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel meta-analysis method. There was no meta-analysis conducted for self-reported Black African ancestry because this would simply duplicate the analysis from South Africa as reported elsewhere in the Figure. Further information on selection of the study participants based on self-reported ancestry appears in the eAppendix in Supplement 1.
aAffected individuals had exfoliation syndrome and unaffected individuals did not have it.
bIncluded participants from Japan and Singapore who self-identified as having Asian ancestry.
cIncluded participants from Austria, Canada, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Poland, Romania, Russia, Spain, Turkey, and the US.
