Figure 4. Dissection of pathological mechanisms of GNAO1 clinical variants.
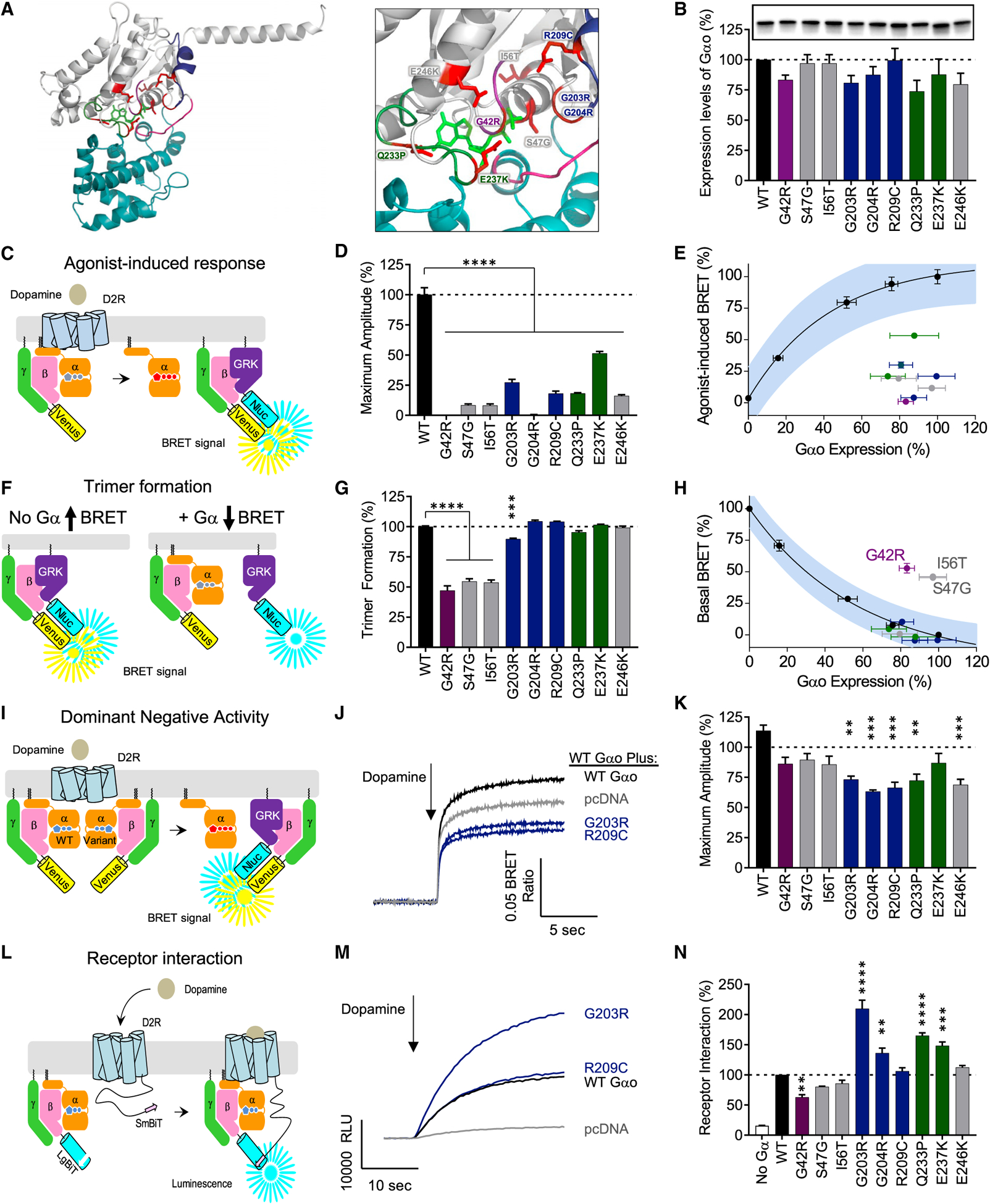
(A) Mapping the genetic variation on the structural model of Gαo. The homology model of Gαo was constructed on the basis of the crystal structure of the Gαi1 (1GP2).
(B) Expression levels of Gαo mutants analyzed by western blotting with anti-Gαo antibody.
(C) The assay design for GPCR-G protein coupling. HEK293T/17 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding FLAG-D2R, Gαo, Venus-Gβ1γ2, and masGRK3ct-Nluc-hemagglutinin (HA). Dopamine application to the transfected cells induces the dissociation of Gαo from Venus-Gβ1γ2, which increases the BRET ratio through the interaction of Venus-Gβ1γ2 with masGRK3ct-Nluc-HA.
(D) Effect of mutations on GPCR-mediated G protein activation.
(E) Correlation analysis of GPCR-mediated G protein activation and Gαo expression levels.
(F) The assay design for trimer formation. In the absence of exogenous Gα subunit, transfected masGRK3ct-Nluc-HA and Venus-Gβ1γ2 produces masGRK3ct-Nluc-HA-bound Venus-Gβ1γ2 and results in high basal BRET signal (left). Exogenous expression of Gαo sequesters Venus-Gβ1γ2 from masGRK3ct-Nluc and decreases the BRET signal (right).
(G) Effect of mutations on trimer formation measured by basal BRET ratio. The ratio obtained without Gαo or with WT Gαo is designated as 0% or 100% trimer formation.
(H) Correlation analysis of trimer formation versus Gαo expression level quantified from western blotting experiments.
(I) The assay design for the dominant-negative activity of Gαo mutants. WT Gαo and mutant Gαo were transfected with FLAG-D2R and BRET sensors. Dominant-negative mutants can suppress the coupling of D2R and WT Gαo.
(J) Time course of agonist-mediated G protein activation. The condition transfected with empty vector, pcDNA3.1(+), mimics a single null allele (gray). The lower activity than this condition indicates the dominant-negative activity of Gα mutants.
(K) Effect of mutations on agonist-mediated G protein activation. The activity of the Gα mutants was compared to the single null allele condition.
(L) The assay design for agonist-induced GPCR-G protein interaction. HEK293T/17 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding D2R-myc-SmBiT, Gαo, LgBiT-Gβ1, and Gγ2. Dopamine application to the transfected cells induces the interaction between dopamine-activated D2R-myc-SmBiT and Go trimer consisted of exogenous Gαo, LgBiT-Gβ1, and Gγ2, resulting in reconstitution of functional Nluc.
(M) Time course of agonist-induced D2R and Gαo interaction.
(N) Effect of mutations on agonist-induced D2R and Gαo interaction (n = 3 experiments).
Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA followed by the Dunnett’s post hoc comparisons with a control. Values represent means ± SEM from three independent experiments, each performed with three replicates. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
