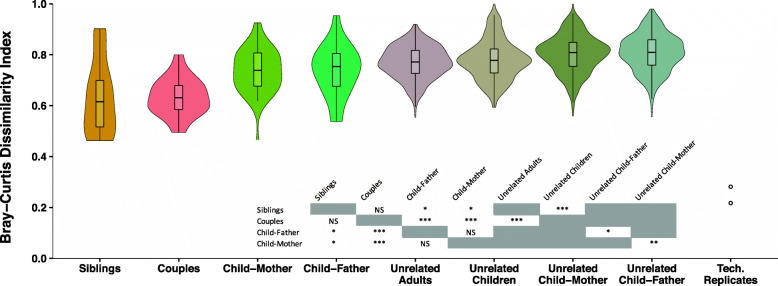
Fig. 5.
Shared environment led to greater similarity between individual’s oral microbial communities at strain level. Comparing microbial community similarities among different family groups, based on saliva/soft tissue swab samples from the extended biological family dataset. Dissimilarities between individuals were lowest among cohabitating couples and siblings, even compared to child-mother and child-father. Children’s oral microbiota were equally similar to their father’s, as they were to their mother’s. Couples and siblings were more similar to themselves, compared to unrelated adults and unrelated children, respectively. Technical replicates were highly similar to one another. Statistical comparisons were performed using Wilcoxon rank sum test and the previously used permutation test (when including unrelated groups)