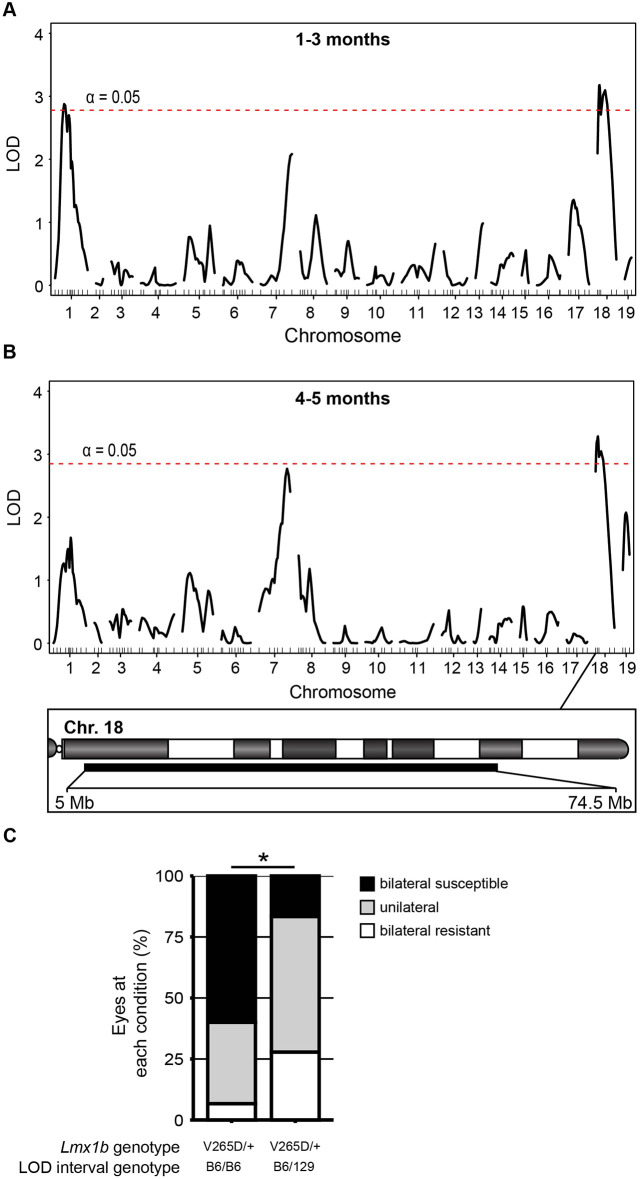
Fig. 6.
Modifier loci. Based on slit-lamp data, individual N2 mice were binned into one of three categories: bilateral susceptible (B6-like), bilateral resistant (129-like) or unilateral. Using these data, a genome-wide one-dimensional quantitative trait locus (QTL) scan was performed. (A) At 1-3 months, intervals on both Chr 1 [33-139 Mb, maximum logarithm of the odds (max LOD) at 53.6 Mb] and Chr 18 (5-71.7 Mb, max LOD at 30.9 Mb) reached genome-wide significance (5% significance threshold, genome-wide corrected, red dashed lines). (B) At 4-5 months, an interval on Chr18 (5-74.5 Mb, max LOD at 30.9 Mb) with the same max LOD as 1-3 months was identified at genome-wide significance. (C) Testing of the modifier locus by comparing Lmx1bV265D/+ mutant mice that are either homozygous (B6/B6) or heterozygous (B6/129) for the Chr 18 intervals. Having a strain 129 genotype throughout the modifier interval significantly increased resistance to severe ocular phenotypes compared to B6 homozygous littermates (Fisher's exact test, *P=0.036). Lmx1b WT mice that are B6/129 heterozygous for the Chr 18 interval did not develop anterior eye phenotypes. We examined 15 (Chr 18 B6/B6) and 18 (Chr 18 B6/129) mice.