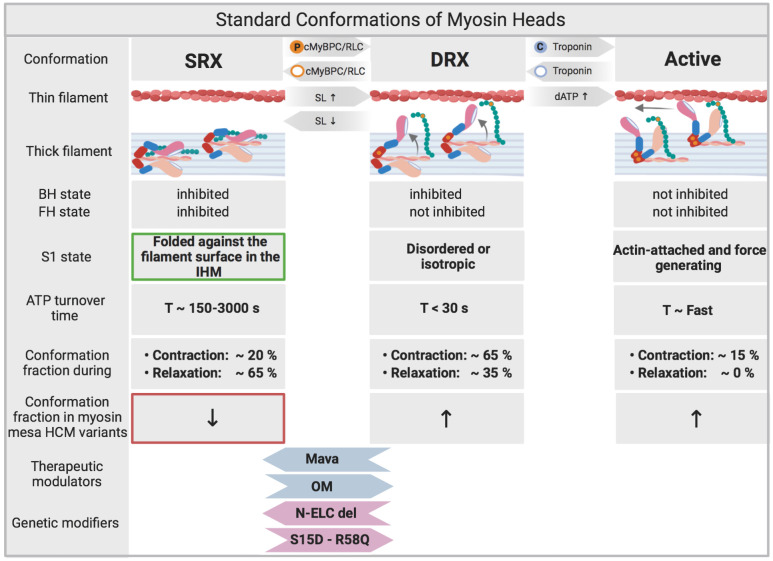
Fig. 3.
Standard conformations of myosin heads. Physiologically the SRX state and DRX state of myosin is balanced and subject to variation depending on regulating mechanisms such as cRLC and cMyBPC phosphorylation as well as sarcomere length (SL). Calcium binding to Troponin allows myosin heads to bind actin. SRX/DRX/Active states are dynamic over the time course of contraction. The majority of myosin heads remain in the SRX conformation during relaxation (Brunello et al., 2020). Reduced myosin SRX occurs in certain HCM causing mutations including those within the myosin mesa (Fig. 2B). Mavacamten (Alamo et al., 2016) has been shown to increase myosin SRX conformations (Rohde et al., 2018) (Anderson et al., 2018; Green et al., 2016; Olivotto et al., 2020). In contrast, Omecamtiv Mecarbil (OM) activates cardiac muscle contraction (Cleland et al., 2011; Malik et al., 2011; Teerlink et al., 2011, 2016) and decreases the proportion of myosin heads in the SRX conformation. Based on that, a recent study has proven OM to have a positive therapeutic impact in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction (Teerlink et al., 2020). N-terminally truncated ELC has been shown to lead to stabilization of myosin SRX (Sitbon et al., 2020). Constitutive cRLC phosphorylation in the MYL2 R58Q variant has been shown to increase DRX myosin (Yadav et al., 2019a).