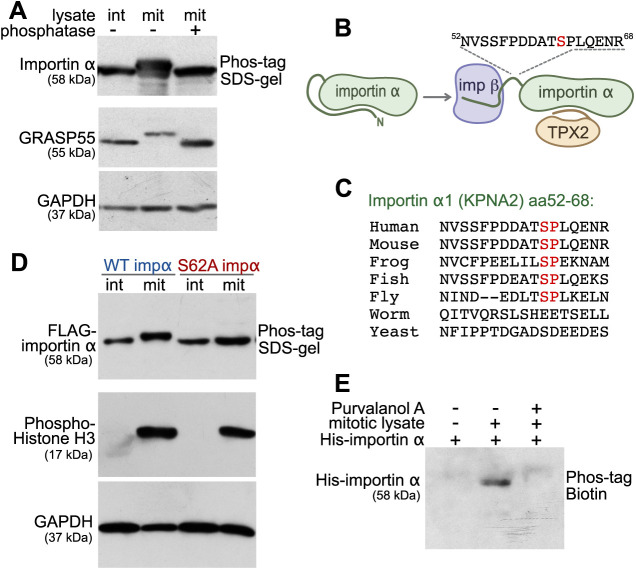
Fig. 1.
Importin α is mitotically phosphorylated at serine 62 by CDK1. (A) Importin α is phosphorylated during mitosis. Cell lysates from interphase (int) and mitotic (mit) HeLa cells, as well as λ phosphatase-treated mitotic lysate, were separated on a 10% SDS gel containing 25 μM Phos-tag acrylamide and immunoblotted for importin α. GRASP55 and GADPH were separated by regular SDS–PAGE. (B) Schematic illustration of the location of the mitotically-phosphorylated peptide identified by mass spectrometry. The identified peptide (residues 52–68) harbors the mitosis-specific phosphorylation site of importin α1 (KPNA2) and is located between the importin β (imp β)-binding domain and the NLS-binding domain. (C) Within the identified peptide sequence, residue serine 62 is conserved among higher eukaryotes. The Ser-Pro sequence matches a CDK1 phosphorylation consensus motif. (D) Importin α (impα) is phosphorylated at serine 62. Interphase or mitotic cell lysates from cells expressing FLAG-tagged WT importin α or importin α S62A were separated on a Phos-tag acrylamide gel and immunoblotted for FLAG. Phospho-histone H3 and GAPDH were separated by SDS–PAGE. (E) Importin α phosphorylation is blocked by the CDK1 inhibitor purvalanol A. Beads coated with recombinant full-length His-tagged importin α were incubated with mitotic HeLa extract in the presence or absence of purvalanol A. The beads were then washed by high-salt buffer (PBS, 1M NaCl), and importin α was eluted by boiling in SDS sample buffer. Phosphorylation was detected by blotting with Phos-tag biotin and streptavidin–HRP. Data in A,D,E are representative of three experiments.