Fig. 4. Gel@MSN/miR-21-5p attenuates adverse LV remodeling and improves pumping effectiveness of the heart after MI.
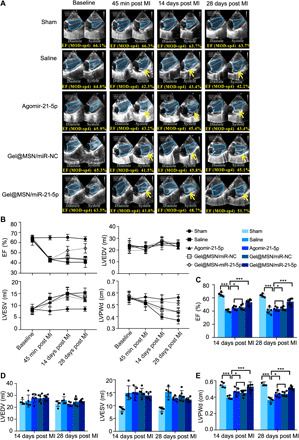
(A) Representative echocardiography imaging by the modified Simpson method of short-axis views for each treatment group at baseline and 45 min, 14 days, and 28 days after MI. The site of the infarct zone is shown by arrows. Notable chamber dilation and wall thinning occurred at 28 days following MI, consistent with the adverse remodeling process. (B) Time course analysis of the EF, LVEDV, LVESV, and LVPWd. (C) MI caused a gradual decline in the EF over 28 days, which was notably attenuated by Gel@MSN/miR-21-5p. (D) MI caused a gradual increase in the LVEDV at day 14 and day 28. The LVEDV of the Gel@MSN/miR-21-5p treatment group was substantially attenuated compared with those of the other three treatment groups. (E) MI caused progressive thinning of the LVPWd thickness at the diastole, which was attenuated by Gel@MSN/miR-NC and agomiR-21-5p treatment and further attenuated by Gel@MSN/miR-21-5p treatment at day 14 and day 28. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.01. Sham, n = 3; MI/saline, n = 5; MI/agomir, n = 5; MI/Gel@MSN/miR-NC, n = 6; and MI/Gel@MSN/miR-21-5p, n = 6. The data are shown as the means ± SD. Photo credit: Yan Li, Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, College of Stomatology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200011, China.
