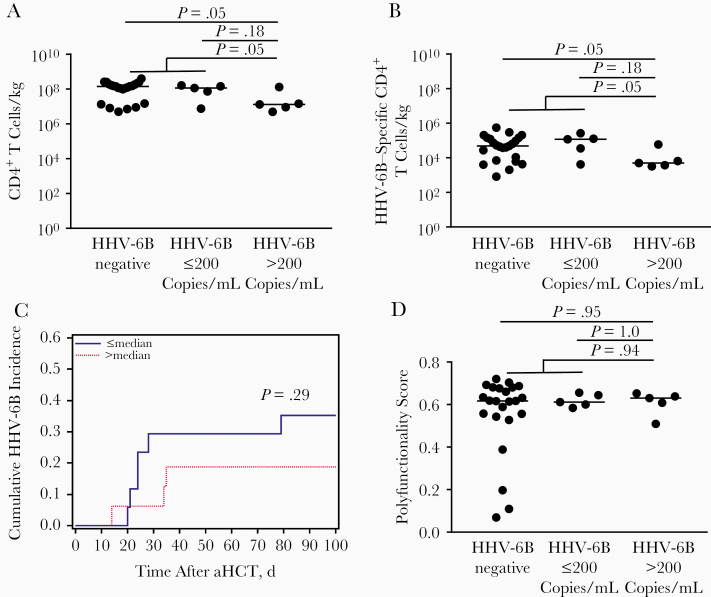
Figure 1.
The quantity of donor-derived total or human herpesvirus (HHV) 6B–specific CD4+ T cells per kilogram, but not the polyfunctionality score, is correlated with reduced HHV-6B detection after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (aHCT). A, B, Patients with a peak HHV-6B viral load above the median (>200 copies/mL) after aHCT received fewer estimated total (A) and HHV-6B–specific (B) CD4+ T cells per kilogram in their hematopoietic cell products than patients with HHV-6B detected at ≤200 copies/mL or with no HHV-6B detection (P values based on Wilcoxon rank sum tests). C, Cumulative incidence plot demonstrates a numerically (but not significantly) lower incidence of HHV-6B in patients who received more than the median versus a lower number of donor-derived HHV-6B–specific CD4+ T cells per kilogram. D, Polyfunctionality scores for these T cells did not differ significantly between patient groups. Circles represent individual patients; horizontal lines, median values.