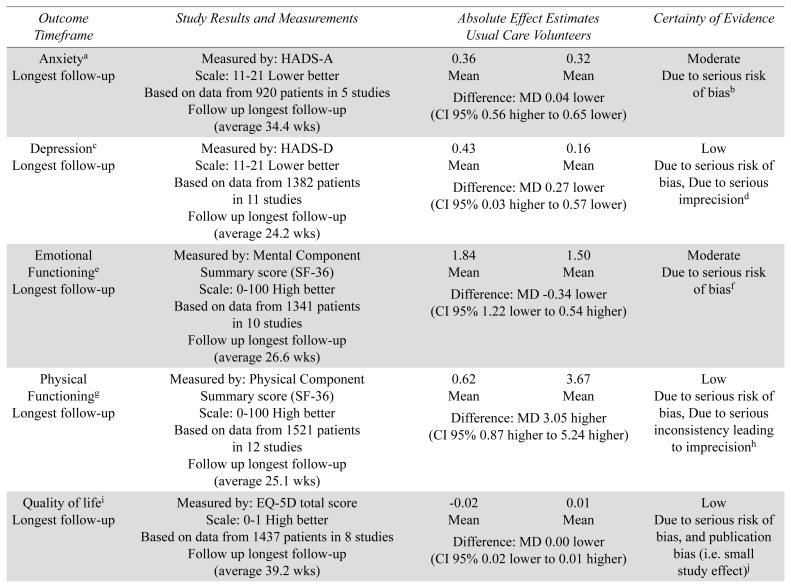
TABLE 2.
GRADE summary of findings
| Outcome Timeframe | Study Results and Measurements | Absolute Effect Estimates Usual Care Volunteers | Certainty of Evidence | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anxietya Longest follow-up | Measured by: HADS-A1 Scale: 11–21 Lower better Based on data from 920 patients in 5 studies Follow up longest follow-up (average 34.4 wks) |
0.36 Mean |
0.32 Mean |
Moderate Due to serious risk of biasb |
| Difference: MD 0.04 lower (CI 95% 0.56 higher to 0.65 lower) | ||||
|
| ||||
| Depressionc Longest follow-up | Measured by: HADS-D Scale: 11–21 Lower better Based on data from 1382 patients in 11 studies Follow up longest follow-up (average 24.2 wks) |
0.43 Mean |
0.16 Mean |
Low Due to serious risk of bias, Due to serious imprecisiond |
| Difference: MD 0.27 lower (CI 95% 0.03 higher to 0.57 lower) | ||||
|
| ||||
| Emotional Functioninge Longest follow-up | Measured by: Mental Component Summary score (SF-36) Scale: 0–100 High better Based on data from 1341 patients in 10 studies Follow up longest follow-up (average 26.6 wks) |
1.84 Mean |
1.50 Mean |
Moderate Due to serious risk of biasf |
| Difference: MD −0.34 lower (CI 95% 1.22 lower to 0.54 higher) | ||||
|
| ||||
| Physical Functioningg Longest follow-up | Measured by: Physical Component Summary score (SF-36) Scale: 0–100 High better Based on data from 1521 patients in 12 studies Follow up longest follow-up (average 25.1 wks) |
0.62 Mean |
3.67 Mean |
Low Due to serious risk of bias, Due to serious inconsistency leading to imprecisionh |
| Difference: MD 3.05 higher (CI 95% 0.87 higher to 5.24 higher) | ||||
|
| ||||
| Quality of lifei Longest follow-up | Measured by: EQ-5D total score Scale: 0–1 High better Based on data from 1437 patients in 8 studies Follow up longest follow-up (average 39.2 wks) |
−0.02 Mean |
0.01 Mean |
Low Due to serious risk of bias, and publication bias (i.e. small study effect)j |
| Difference: MD 0.00 lower (CI 95% 0.02 lower to 0.01 higher) | ||||
| Physical Activity Longest follow-up | Measured by: MET (energy/kg/mns/wk); MVPA per week; minutes spent on exercise Scale: - High better Based on data from 1349 patients in 6 studies (average 10.2 months) |
Mean | Mean | Low Due to serious risk of bias and indirectnessk |
| Difference: SMD 0.48 more (CI 95% 0.14 more – 0.83 more) | ||||
|
| ||||
| Frequency of Hospital Admissions | Measured by: Narrative report: Admission rate not provided(37) and mean hospital admission rate per 1000 participants(58) | 2 studies reported hospitalization frequency. One qualitative report of no significant difference between groups.(37) Another study reported the incidence of hospitalization as (27.9/1000) in the intervention group versus (30.13/1000) control group (p = < .01) (58) | Low Due to serious risk of bias and inconsistencyl |
|
|
| ||||
| Falls | Measured by: Narrative report: Proportion of participants reporting one or more falls in the past 3 months (fallers)(51) and the incidence of falls(54) | 2 studies reported falls. One RCT reported the difference between proportion of fallers in the intervention group (14/35) versus (8/19) in the control group (P= 0.11)(51) Another study (cluster RCT) reported the incidence of falls in the intervention population (100/183) versus (158/217) in the control population (p = < .01)(54) | Low Due to serious risk of bias and inconsistencym |
|
|
| ||||
| Adverse Events | Narrative summary (results not pooled) | 6 studies reported adverse events, no events or no difference between groups was found(32,34,46,54,57) | Low Due to serious risk of bias and inconsistencyn |
|
HADS = Hospital Anxiety-Depression-Depression; HADS-A = Hospital Anxiety Depression-Anxiety; MET = Metabolic Equivalent Task, Energy used/per Kg/minute/week; MVPA +Time spent in moderate to vigorous physical activity.
All Measures converted to HADS-A.
Anxiety: Risk of bias: Serious. Inadequate/lack of blinding of outcome assessors, resulting in potential for detection bias, Incomplete data and/or large loss to follow up; Inconsistency: Serious. Imprecision: Not serious. Wide confidence intervals; decided not to rate down further for imprecision as it is due to inconsistency.; Publication bias: Not serious. Not assessed due to small number of studies.
All measures converted to HADS-D.
Depression: Risk of bias: Serious. Inadequate/lack of blinding of outcome assessors, resulting in potential for detection bias, Incomplete data and/or large loss to follow up.; Inconsistency: Serious. Point estimates vary widely, The confidence interval of some of the studies do not overlap with those of most included studies/ the point estimate of some of the included studies.; Imprecision: Not serious. Decided not to rate down for imprecision as it is mostly due to inconsistency.
Emotional Function: Risk of bias: Serious. Inadequate concealment of allocation during randomization process, resulting in potential for selection bias, Inadequate/lack of blinding of outcome assessors, resulting in potential for detection bias, Incomplete data and/or large loss to follow up; Inconsistency: Not serious. Decided not to rate further down as the observed heterogeneity seems to be due to risk of bias; Imprecision: Serious. Wide confidence intervals.
All measures converted to PCS score.
Physical Function: Risk of bias: Serious. Inadequate concealment of allocation during randomization process, resulting in potential for selection bias, Inadequate/lack of blinding of outcome assessors, resulting in potential for detection bias, Incomplete data and/or large loss to follow up.
All measures converted to EQ-5D total score.
Quality of Life: Risk of bias: Serious. Incomplete data and/or large loss to follow up; significant test of interaction for the subgroup of low vs. high risk of bias due to missing participants data.; Publication bias: Serious. Asymmetrical funnel plot with evidence of small study effect.
Physical Activity: Risk of bias: Serious. Inadequate concealment of allocation during randomization process, resulting in potential for selection bias, Inadequate/lack of blinding of outcome assessors, resulting in potential for detection bias, Incomplete data and/or large loss to follow up; Inconsistency: Not serious. Decided not to rate further down as the observed heterogeneity seems to be due to risk of bias; Indirectness: Serious, Publication bias: Not serious. Less than 10 studies.
All measures converted to MCS.
Hospital admission: Risk of bias: Serious. Inadequate concealment of allocation during randomization process, resulting in potential for selection bias, inadequate/lack of blinding of outcome assessors; Inconsistency: Serious Uncertain effects narrative summary.
Falls: Risk of bias: Serious. Inadequate concealment of allocation during randomization process resulting in potential for selection bias; Inconsistency: Serious. Uncertain effects with narrative summary.
Averse events: Risk of bias: Serious. Inadequate/lack of blinding of assessors resulting in potential for detection bias, incomplete outcome reporting. Inconsistency: Serious Uncertain effects narrative summary.