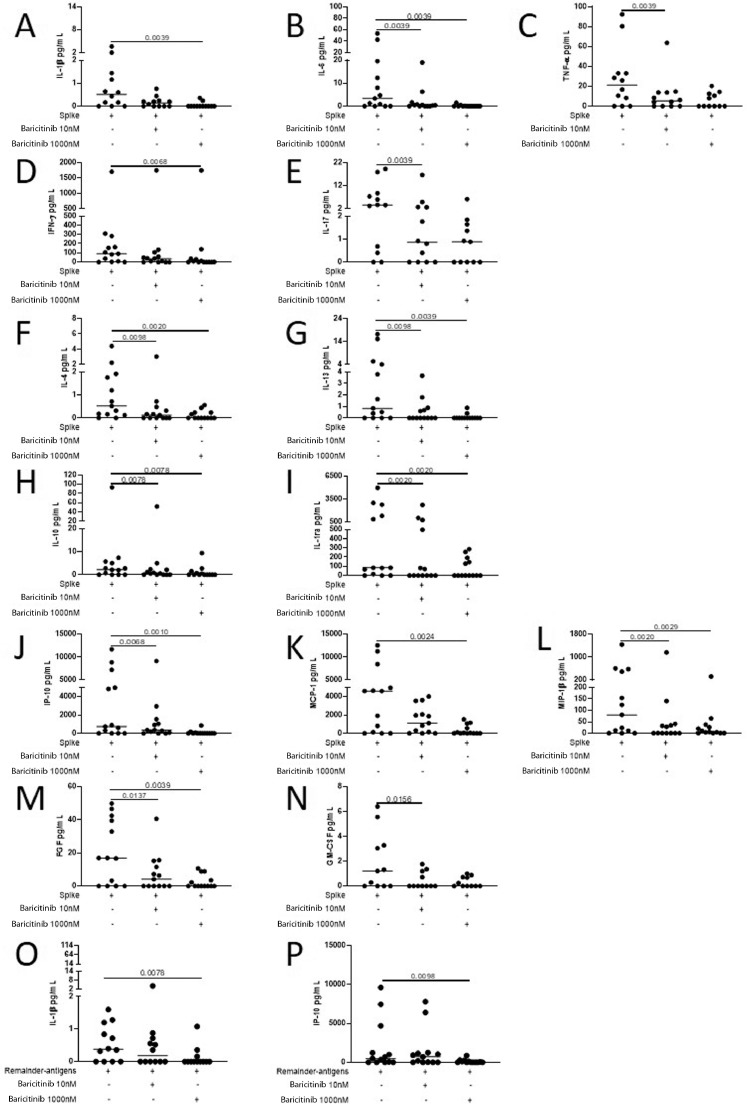
Fig. 3.
In COVID-19 patients, the exogenous addition of baricitinib decreases the in vitro levels of pro-inflammatory, Th1, Th17, Th2 cytokines, immunomodulatory factors, chemokines and growth factor in response to SARS-Cov-2 peptides. Evaluation of 27 analytes in response to spike and to remainder-antigens by multiplex technology. In COVID-19 patients baricitinib at 1000 nM significantly decreases the in vitro cytokine spike-specific response mediated by the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α (A-C), the Th1- and Th17-cytokines IFN-γ and IL-17 (D-E), the Th2-cytokines IL-4 and IL-13 (F-G), IL-10 and IL-1ra (H-I), the chemokines IP-10, MCP-1 and MIP-1β (J-L) and the growth factors FGF and GM-CSF (M-N). Baricitinib at 1000 nM decreased also IL-1β and IP-10 production in response to remainder-antigens (O-P). Analyte levels measured by luminex in stimulated plasma. The horizontal lines represent the median; statistical analysis was performed using the Wilcoxon test, and p value was considered significant if ≤0.016. Footnotes: IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor Necrosis Factor; IFN: Interferon; ra: receptor antagonist; IP: interferon-inducible protein; MCP: monocyte chemoattractant protein; MIP: macrophage inflammatory protein; FGF: fibroblast growth factor; GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor.