Figure 1.
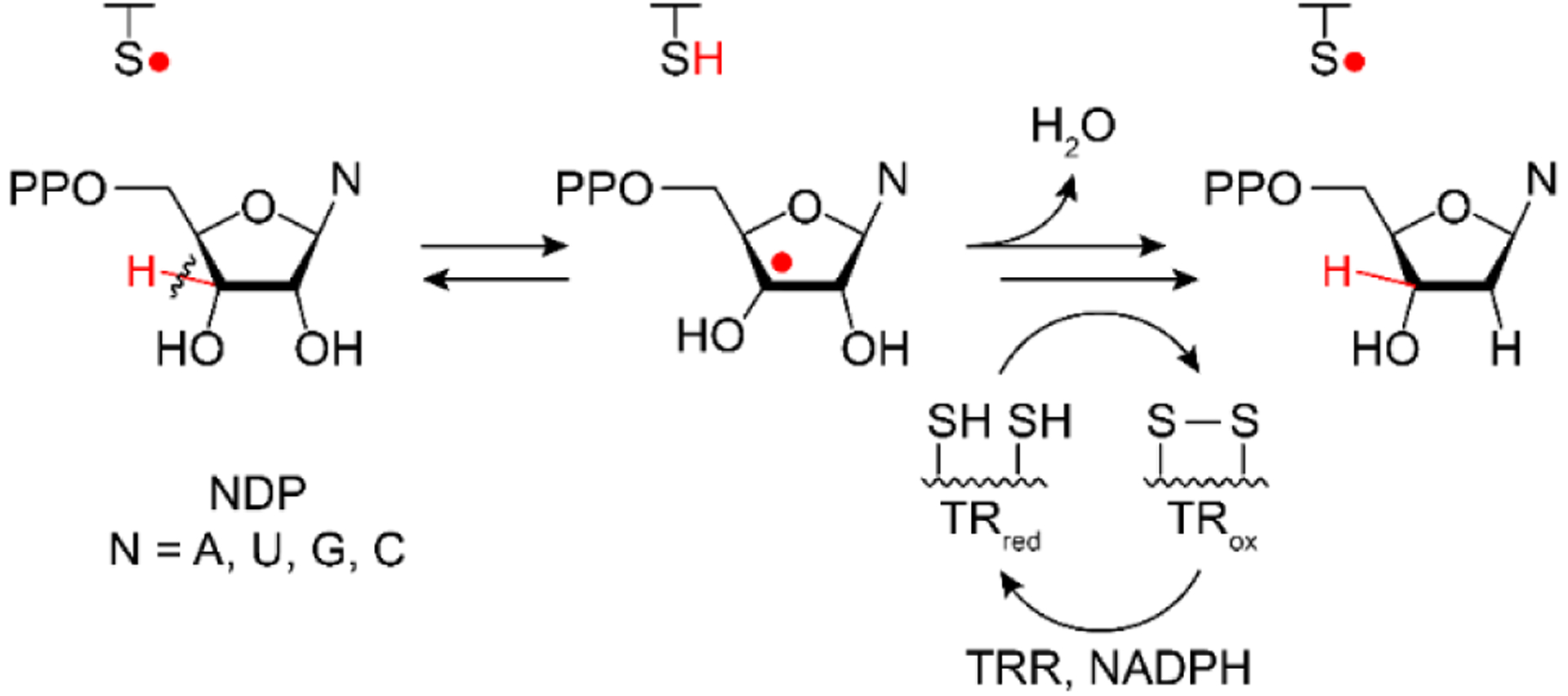
Ribonucleotide reductase function. Nucleotides are “activated” for reduction by a cysteine based thiyl radical mediated H-atom abstraction from the 3′-C. The substrate radical is then reduced, losing water from the 2′-C, by two cysteines in the active site that form a disulfide bond. Re-reduction of disulfide by the thioredoxin (TR), thioredoxin reductase (TRR), and NADPH system regenerates the active site for subsequent turnover. Thiyl radical generation occurs through radical transfer and is the basis for class and sub-class differentiation. Adapted from reference 1.
